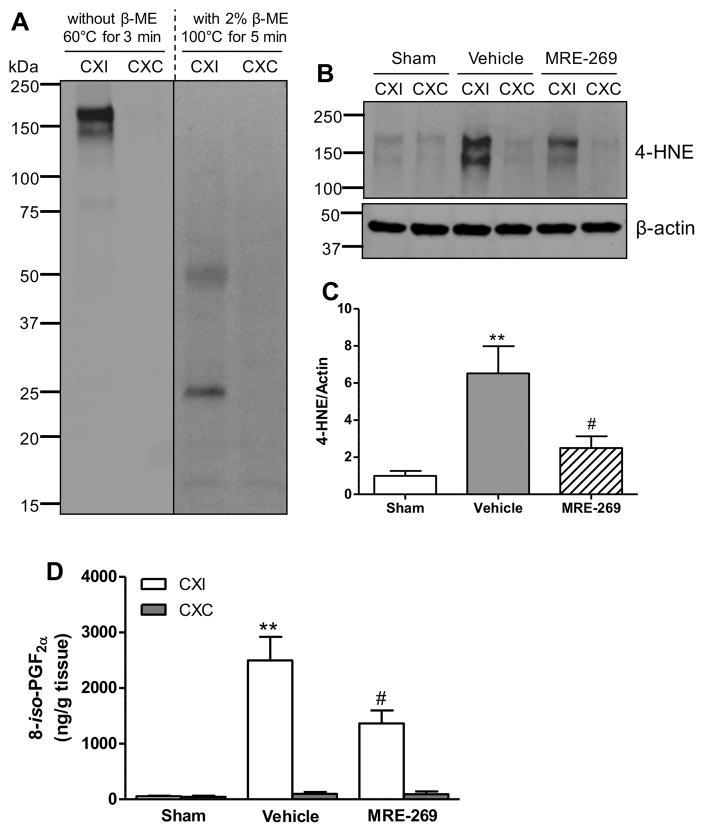
Figure 5. MRE-269 reduced oxidative damage as assessed by levels of 4-HNE and 8-iso-PGF2α in aged rats following transient MCAO.
A) Immunoblot for 4-HNE under non-reduced and reduced conditions in the cortex of aged rat brain subjected to stroke, which shows better signal of 4-HNE under the non-reduced conditions. B) Immunoblot for 4-HNE in the cortex of sham-, vehicle- and MRE-269- treated rats. C) Transient MCAO significantly increased 4-HNE protein level in the ischemic cortex compared to the sham rats, and the 4-HNE level was dramatically decreased in the MRE-269-treated rats compared to the vehicle group. D) Delayed treatment with MRE-269 (0.25 mg/kg) significantly reduced 8-iso-PGF2α content in the ischemic cerebral cortex at 18 h following transient MCAO. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM, **P<0.01 versus sham and #P<0.05 versus vehicle. Sham, n=5; Vehicle, n=12; MRE-269, n=13. CXI = cortex ipsilateral to stroke; CXC = cortex contralateral to stroke.