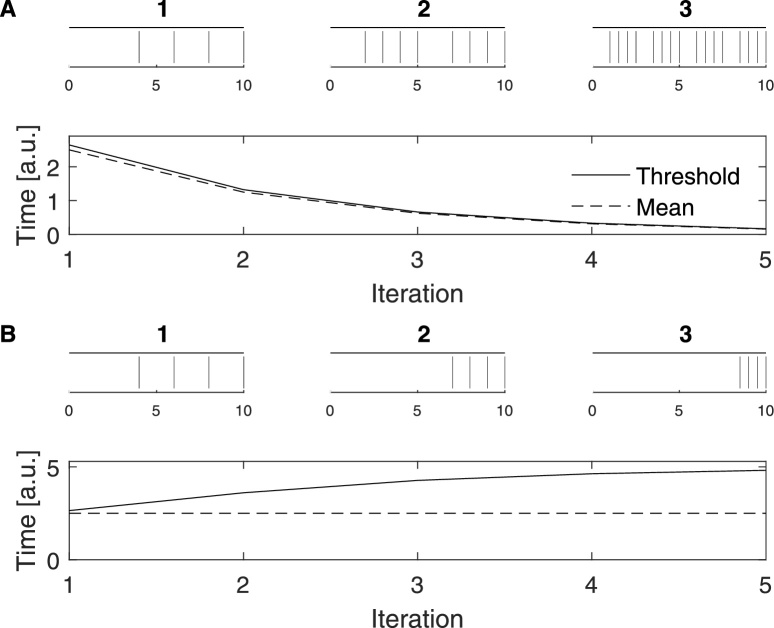
Fig. 4.
Threshold value vs. the mean of the ISI-distribution. (A) Dependence on the number of spikes (first criterion). In each iteration the number of spikes is increased by concatenating two half-length copies of the previous iteration. Both the mean and the threshold decrease with spike count. (B) Dependence on the ISI-distribution (second criterion). From iteration to iteration the ISI-distribution is changed by halving the three short ISIs and prolonging the long ISI accordingly. Since the spike count (and thus the number of ISIs) is kept constant, the mean does not respond to this change. However, the threshold correctly increases with the heightened importance of the long ISI.