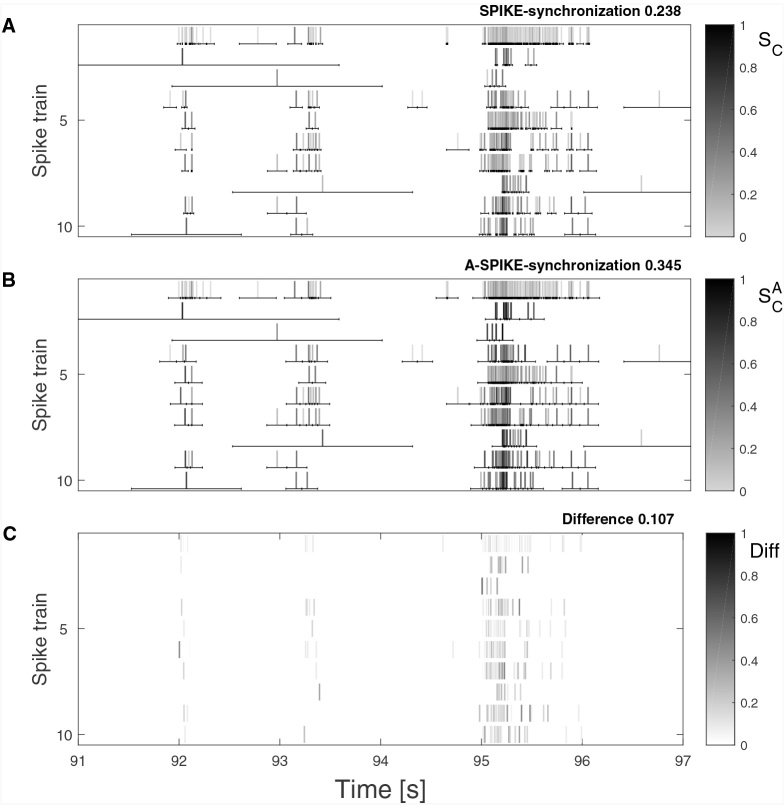
Fig. 8.
Real data example from MEA recordings (see Appendix B.1 for more details). Ten spike trains from the dataset are plotted and their coincidence windows are drawn as obtained by SPIKE-synchronization (A) and A-SPIKE-synchronization (B). The difference is plotted in (C). Due to the adaptive coincidence windows, A-SPIKE-synchronization is able to match around 45% more spikes between bursting spike trains than SPIKE-synchronization. As in Fig. 3, the color scale is gray-black in (A) and (B) and white-black in (C).