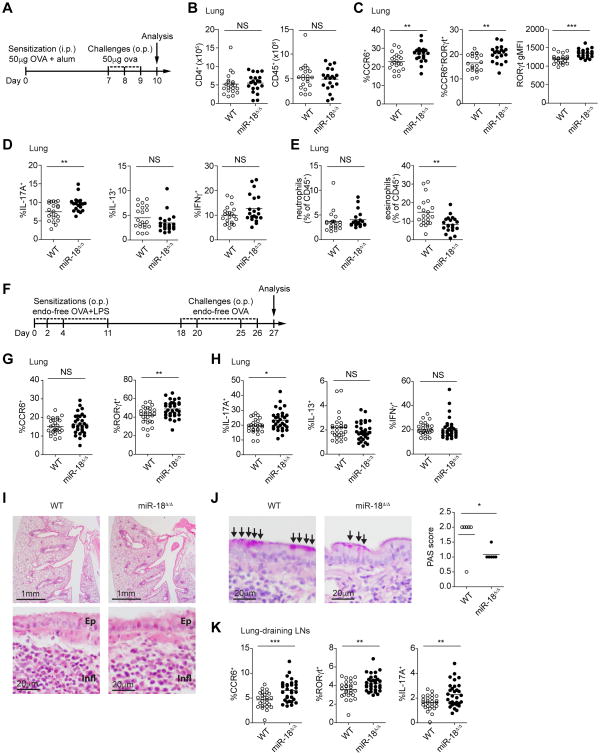
Figure 4. miR-18a deficiency increases lung Th17 cell frequencies in airway inflammation models.
(A) Schematic of the 10-day in vivo airway hypersensitivity model with intraperitoneal (i.p.) OVA+alum sensitization on day 0, followed by three consecutive daily challenges with OVA oropharyngeally (o.p.) on days 7, 8, and 9. On day 10, cells from the lungs of WT and miR-18Δ/Δ mice were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Total CD4+ T cell and total CD45+ leukocyte numbers per lung. (C) Frequencies of CCR6+ and CCR6+RORγt+ cells; intracellular RORγt expression levels as determined by gMFI. (D) Frequencies of IL-17A, IL-13 or IFNγ-producing cells among CD4+ T cells after restimulation with PMA/ionomycin. (E) Frequencies of inflammatory cells in the lungs, including eosinophils (CD11b+SiglecF+) and neutrophils (CD11b+Ly6G+). (F) Schematic of the 27-day in vivo airway hypersensitivity model with OVA+LPS sensitizations on days 0, 2, 4, and 11 by oropharyngeal instillation (o.p.), followed by OVA challenge on days 18, 20, 25, and 26. On day 27, cells from the lungs of WT and miR-18Δ/Δ mice were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry. (G) Frequency of CCR6+ and RORγt+ cells among CD4+ T cells.(H) Frequency of IL-17A, IL-13, andIFNγ-producing cells among CD4+ T cells after restimulation with PMA/ionomycin. (I) Hematoxylin and eosin stainings of lungs derived from challenged WT and miR-18Δ/Δ mice. Two different magnifications are shown. Bronchiole epithelium (Ep) and mixed local inflammation (Infl) are marked for orientation in high power fields. (J) Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining highlighting goblet cell metaplasia of the respiratory epithelium (arrows). Histological scores of PAS staining quantifying mucus-secreting cells are quantified in the bar graph. (K) Lung-draining lymph nodes were analyzed by flow cytometry for the frequency of CCR6+ and RORγt+ cells as well as the frequency of IL-17A among CD4+ T cells after restimulation with PMA/ionomycin. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 (two-tailed unpaired t-test with pre-assigned littermate pairs). Data are pooled from three independent experiments, each with three to nine mice per genotype (n=21 mice total per genotype; A-E) or each with seven to twelve mice per genotype (n=26 to 31 mice total per genotype; F-H, J, K). Data in I is a representative experiment with six mice per genotype.