Fig. 7.
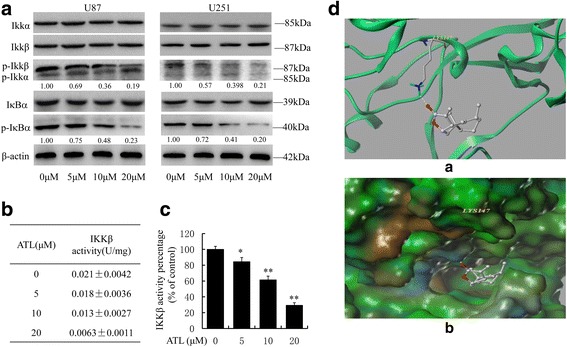
ATL suppresses IKKβ activity by targeting the ATP binding site. a: At 48 h after treatment, we observed the expression levels of IκB-α, p-IκB-α, IKKα/β, and p-IKKα/β by Western blotting in U87 and U251 cells. b-c: At 48 h after treatment, we also assessed IKKβ kinase activity in vitro using a cell IKKβ kinase activity spectrophotometry quantitative detection kit in U87 cells. The specific protocol was described in the “Materials and Methods” section, and the activity value and percentage were calculated using the provided formula. The results are represented as the mean ± SD of three experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. the DMSO-treated group. d: The best ranked position of ATL in the ATP binding site of IKKβ generated docking. (a) Interactions of ATL and IKKβ are delineated by the ribbon structure, hydrogen bonds are displayed as yellow dashed lines, and the participating amino acid residues are marked. (b) MOLCAD representation of the molecular lipophilic potential surface upon the bioactive position of ATL in the ATP binding site of IKKβ. The moieties are denoted as blue for hydrophilic, brown for lipophilic and green for neutral
