Fig. 1.
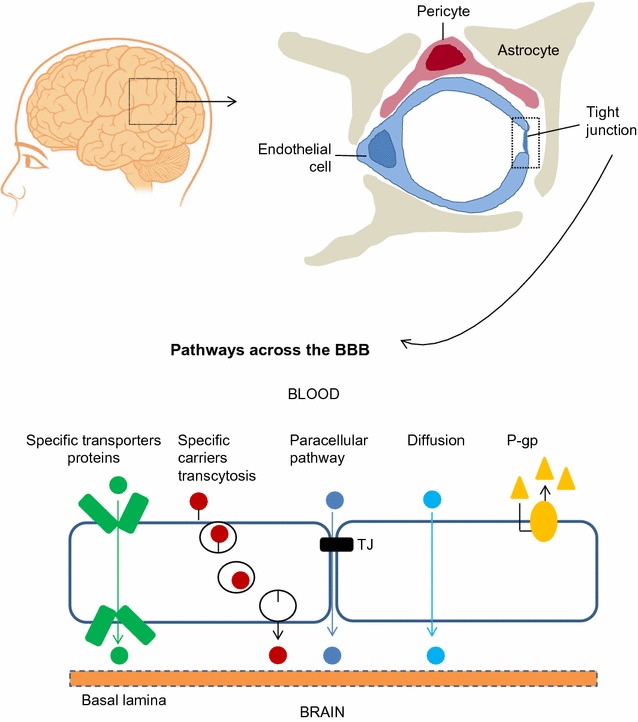
Cellular constituents of the blood–brain barrier. The blood–brain barrier is formed by brain endothelial cells, which are connected by tight junctions. The endothelium, together with the basal lamina, pericytes, and astrocytic end-feet forms the neurovascular unit. Transport pathways across blood brain barrier. Endothelial cells of the BBB have a crucial role in the transport of ions and solutes into and out of the brain. Some substances diffuse freely into and out of the brain parenchyma (O2 and CO2), others such as nutrients need specific transporters, while molecules such as insulin, leptin and transferrin are transported by receptor-mediated transcytosis. P-gp P-glycoprotein, TJ tight junction
