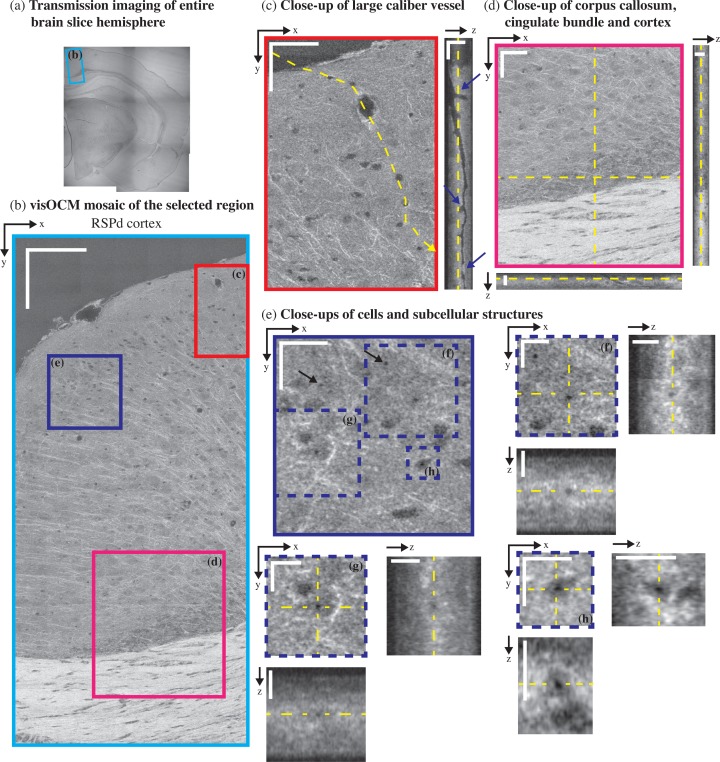
Fig. 5.
ex-vivo visOCM imaging of the RSPd cortex in a B6SJL/f1 mouse brain slice. (a) A transmission image of the entire half hemisphere was performed to locate part of the RSPd cortex (blue rectangle). A mosaic of the area of interest was then obtained with visOCM (b), where one can appreciate the presence of fibers, vessels and cells. A large penetrating vessel (c) can be observed through the difference in contrast between its hollow lumen and the back-scattering of the surrounding tissue. Examples of bifurcations and potential clogging of the vessel are pointed by arrowheads in the orthogonal view (a depth scan is shown in Visualization 2 (3.5MB, AVI) ). Fibers appear as thin oriented bright structures and are present in the cortex and in the corpus callosum (d). Finally, sub-cellular features can also be observed as darker spots within the cell bodies, as shown in (e–h) and pointed by arrowheads in (e). Scalebars: 150 μm in (b), 50 μm in the en-face view of (c–d), 20 μm in the orthogonal views of (c–d) and in the en-face view of (e), 10 μm in the en-face and orthogonal views of (f–g).