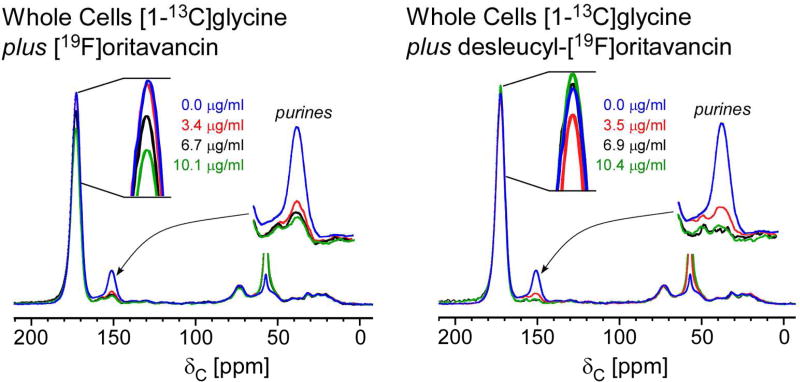
Figure 2.
13C full-echo NMR spectra of S. aureus grown in SASM containing [1-13C]glycine and L-[ε-15N]lysine treated with [19F]oritavancin (left) and desleucyl-[19F]oritavancin (right). The spectra are normalized to equal integrated peak intensity between 10 and 30 ppm to approximate equal aliphatic-carbon content. The [1-13C]glycine incorporation into proteins and peptidoglycan appears at 172 ppm, and the metabolism of glycine via purine biosynthesis, at 153 ppm. The addition of [19F]oritavancin and desleucyl-[19F]oritavancin to S. aureus during growth inhibited purine biosynthesis.