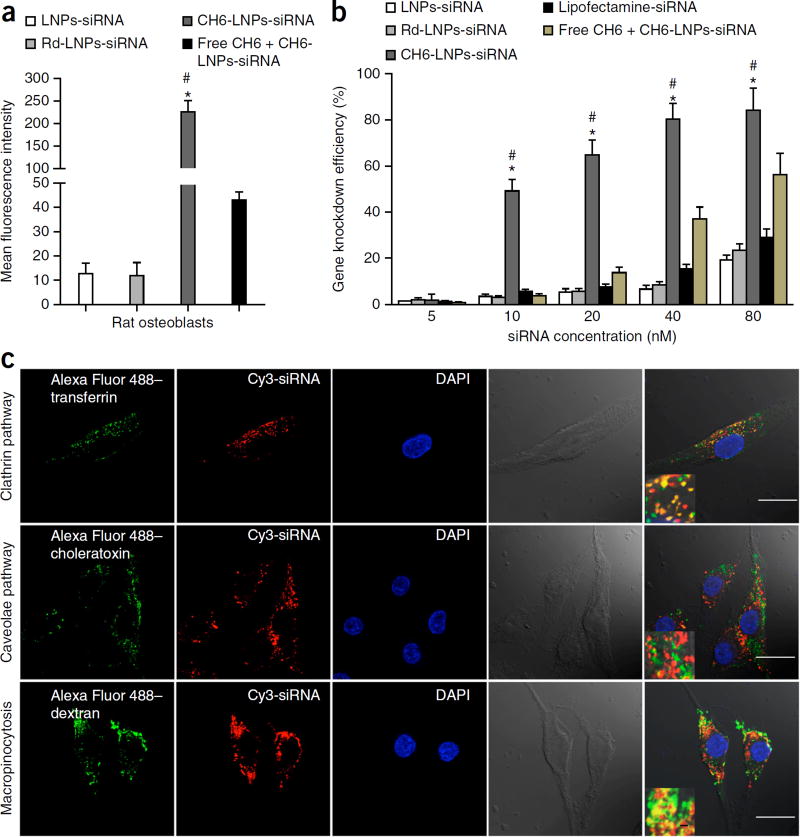
Figure 2.
Cellular selectivity, gene knockdown efficiency and mechanism of cellular uptake of various siRNA formulations. (a) Cellular selectivity: fluorescence intensity of FAM-labeled siRNA in rat primary osteoblasts incubated with LNPs-siRNA, Rd-LNPs-siRNA, CH6-LNPs-siRNA and free CH6 + CH6-LNPs-siRNA. (b) Gene knockdown efficiency: percentage changes of gene expression were quantified after the incubation of the siRNA formulations as described in a as well as the positive control Lipofectamine 2000–siRNA with rat primary osteoblasts. The data are presented as the mean ± sd; n = 3 per group. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with LSD’s post hoc test was performed to determine inter-group differences. (c) Pathway for the cellular uptake of CH6-LNPs-siRNA: intracellular co-localization of Cy3-labeled Plekho1 siRNA (red) and Alexa Fluor 488–labeled endocytic markers (transferrin, choleratoxin and dextran; green) in rat primary osteoblasts. The nucleus was counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 25 µm, large panels and 1 µm, insets. Fourth column, bright-field images of osteoblasts; last column, merged images from all columns. *P < 0.05 for a comparison of CH6-LNPs-siRNA with either LNPs-siRNA or Rd-LNPs-siRNA; #P < 0.05 for a comparison of CH6-LNPs-siRNA with free CH6 + CH6-LNPs-siRNA.