Figure 1. Mutational landscape of CBF-AML.
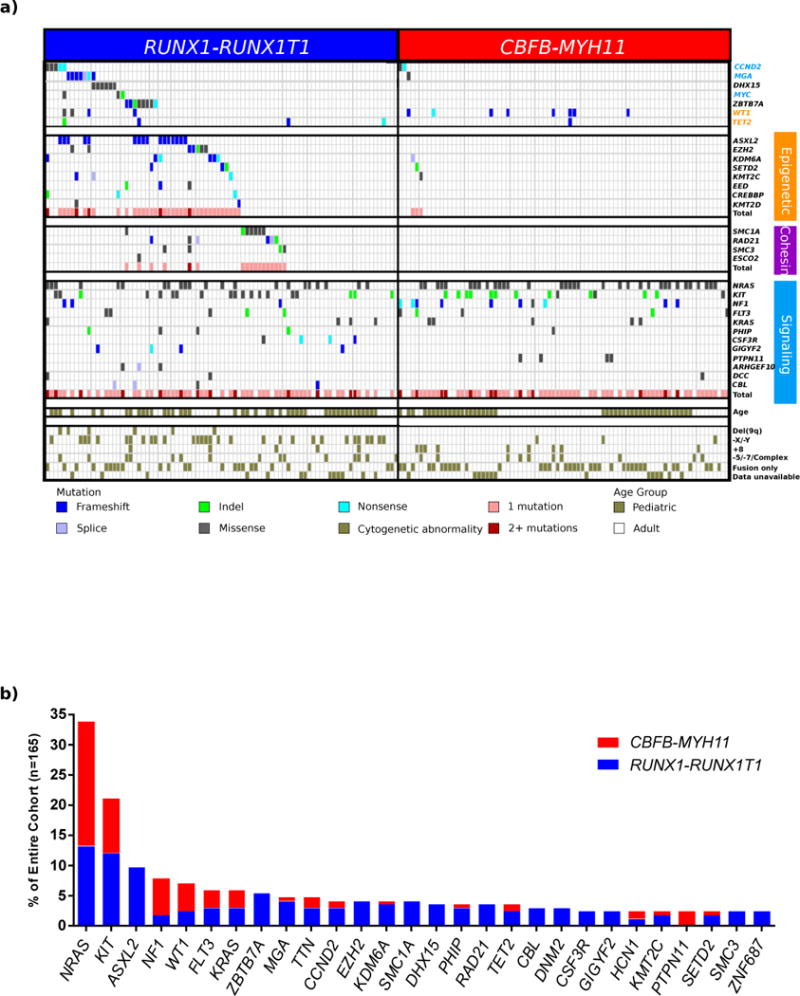
(a) Mutational data for 165 CBF-AML cases sequenced either by whole genome (n=17) or whole exome sequencing (n=148). Signaling, epigenetic, and cohesin genes are grouped into functional groups. Cytogenetic abnormalities and patient age group (adult or pediatric) are shown along the bottom of the figure. Mutations in both epigenetic (p=4.3E–10) and cohesin (p=2.2E–16) genes are significantly enriched in RUNX1-RUNX1T1 AML (Fisher’s Exact test). (b) The frequency of recurrently mutated genes (n>3) separated by CBF-AML fusion type is shown. Of the 10 FLT3 mutations, 4 are internal tandem duplications (ITD), 5 are located in the tyrosine kinase domain, and 1 is classified as neither ITD nor TKD.
