Figure 3.
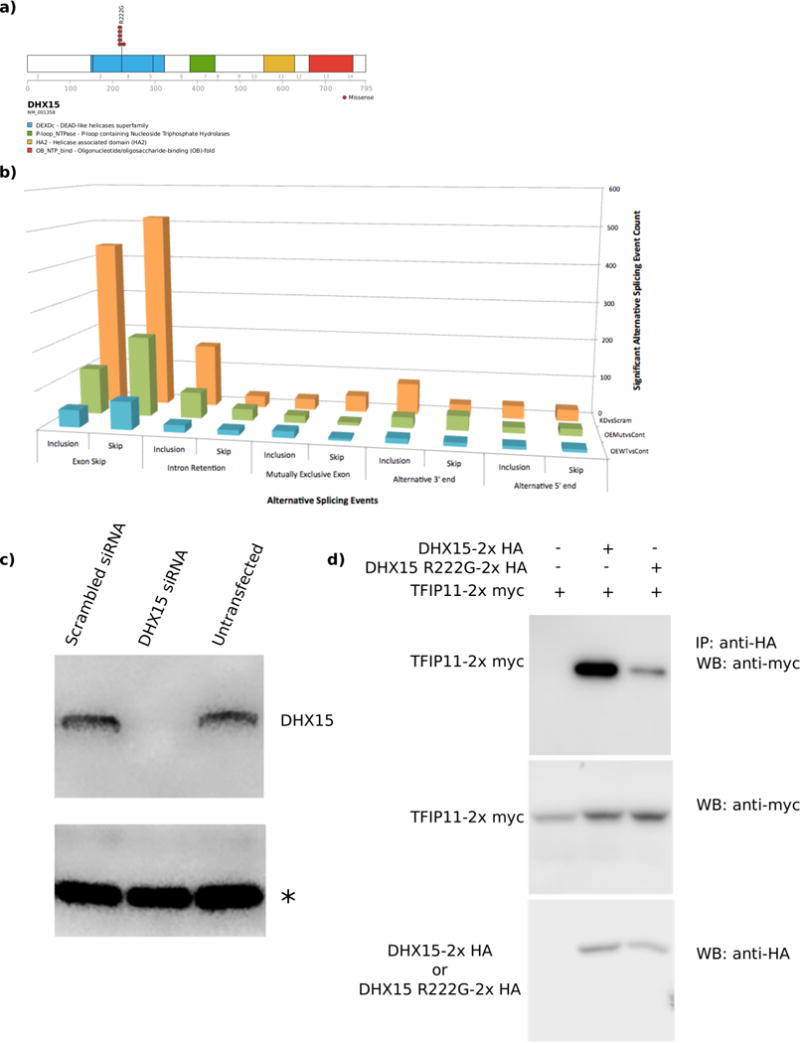
DHX15 is recurrently mutated in RUNX1-RUNX1T1 AML. (a) Domain structure and the localization of mutations for DHX15. (b) Increased numbers of alternative splicing events were observed upon DHX15 knockdown (red bars) or overexpression of the R222G mutant (green bars) compared to overexpression of wildtype DHX15 (blue bars). (c) siRNA mediated knockdown of DHX15 leads to an enrichment of differentially regulated genes associated with splicing and ribosomal biogenesis. (d) Western blot showing the effectiveness of the DHX15 knockdown. Equal amounts of protein were loaded for each sample. An asterisk indicates a non-specific band also used as a loading control. (e) Co-immunoprecipitation of TFIP11 with DHX15 demonstrates reduced binding of TFIP11 to the R222G mutant form of DHX15.
