Figure 1. Live GBS and antibiotic-killed GBS induce activation of PKD1.
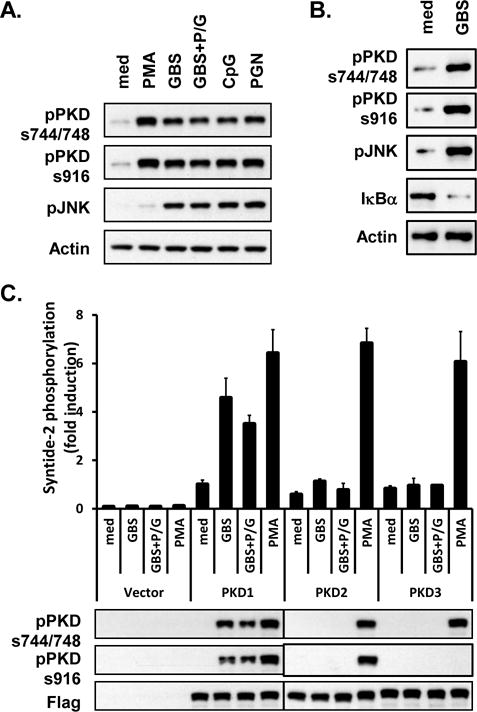
(A) RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with medium (med), PMA (10 ng/ml), live GBS (108 cfu/ml; GBS), antibiotic-killed GBS (108 cfu of GBS were treated with 1 mg of penicillin G for 6 h; GBS+P/G), CpG DNA (12 μg/ml), or PGN (1 μg/ml) for 45 min. (B) THP1 cells were stimulated with medium (med) or live GBS (1 × 108 cfu/ml; GBS) for 1 hr. Phosphorylation status of PKD (pPKDs744/748, pPKDs916) and JNK (pJNK), and protein levels of IκBα were detected by Western blot assay. Actin was used as a loading control. (C) RAW264.7 cells stably expressing empty vector, FLAG-tagged PKD1, FLAG-tagged PKD2, or FLAG-tagged PKD3 were stimulated with medium, live GBS or antibiotic-killed GBS for 45 min. Lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG Ab. Kinase activity of PKD was analyzed in vitro using syntide-2 as a PKD substrate (Top). Expression and phosphorylation status of PKD were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG or anti-phospho-PKD Abs (Bottom). All experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results.
