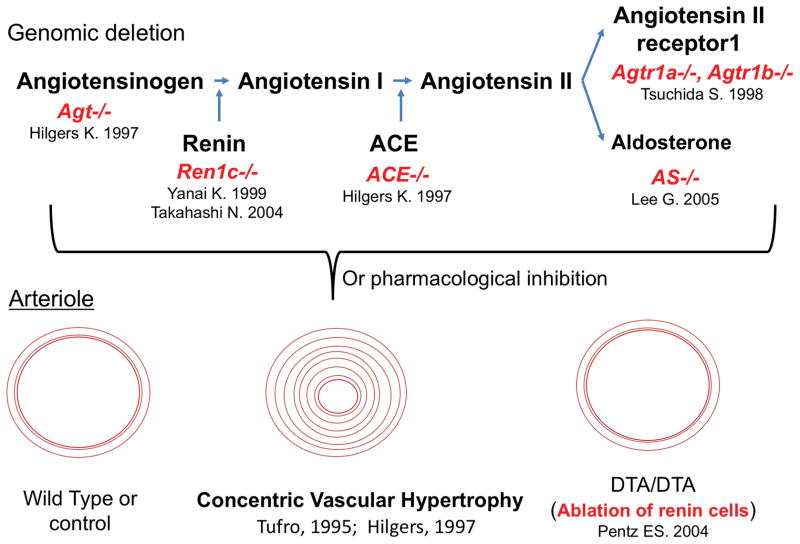
Figure 1. Inactivation of the RAS in early life leads to marked abnormalities in kidney vascular development.
A central feature in all the manipulations is the presence of concentric vascular hypertrophy of the renal arterioles. The lesion does not occur if the renin cells are ablated with diphtheria toxin subunit A (DTA) targeted to the renin gene suggesting that renin cells per se are responsible for the pathology. The same vascular alteration is also seen in humans with renin gene mutations, see text for details. Agt, angiotensinogen; Ren1c−/−, renin gene deletion, ACE−/−, angiotensin converting enzyme deletion,; Agtr1a−/−, Agtr1b−/−, double deletion of angiotensin receptors subtypes A and B. AS−/−, aldosterone synthase KO