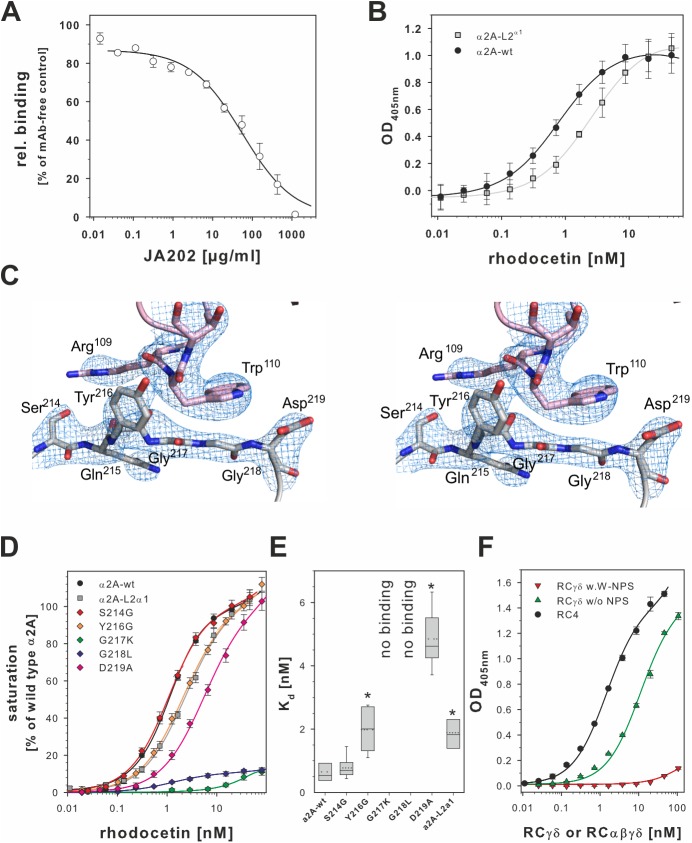
Fig 7. Loop 2 of the α2A domain is the interaction site for the RCγ subunit.
(A) Loop 2 of α2A is an additional binding site for rhodocetin (RC). It contains the epitope for the monoclonal antibody (mAb) JA202, which inhibits binding of RC to immobilized α2A. Bound RC was quantified by ELISA, and values were normalized to noninhibited controls. One set of inhibition curves out of 3 independent experiments with each measurement made in triplicate and the means ± SD for each data point are shown. (B) The α2A loop 2 sequence was replaced with the homologous sequence VGRGGRQ of integrin α1 (α2A L2α1 mutant). The binding-irrelevant antibody JA218 was immobilized to capture wild-type (wt) α2A and α2A L2α1. They were titrated with RC, and bound RC was quantified as in (A). One set of titration curves out of 4 independent experiments, each done in triplicates, is shown with the means ± SD indicated. The α2A L2α1 mutant (light gray ■) significantly reduced affinity for RC compared to the wt (●) (p = 0.0013, two-tailed t test) (C) Stereo view of the α2A loop 2 sequence in contact with the RCγ contact site. The Sigma-A weighted 2Fo-Fc map is shown at 1.5σ contour level. The 2 glycine residues, G217 and G218, form the bottom of a shallow dimple, which is flanked on either side by the side chains of Y216 and D219, in addition to residue N154 of loop 1 (not shown). The indole side chain of W110γ stacks directly above this dimple and interacts with the main chain of the 2 glycine residues. (D) Point mutation analysis of the α2A loop 2 sequence S214QYGGD219. The binding activity of these mutants for RC was tested as in (B). Binding signals taken from at least 7 independent titration curves for each mutant were normalized to the saturation signal of wild type α2A. Means ± SEM are shown for the mutants (◆ of different colors) in comparison to wt (●) and the α2A L2α1 mutant (light gray ■). This analysis showed that the 2 glycines at position 217 and 218 were key to the RCγδ-α2A interaction, as only mutations abrogated α2A binding. (E) The Kd values of the loop 2 point mutations for binding to RC as derived from (D). At least 7 titration curves were evaluated for each mutant. The Kd values were pairwise compared to the Kd value of the wild type α2A domain in a two-tailed Student t test. Significant difference (p < 0.02) is asterisked (*). (F) Modification of tryptophan residues of RCγδ with 2-nitrophenyl sulfenylchloride (NPS-Cl) showed that W110γ is required for α2A domain binding. The wells of a microtiter plate were coated with 10 μg/ml α2A domain and titrated with RCαβγδ (●), with nonmodified RCγδ (green ▲) and with RCγδ with chemically modified W110γ (W-NPS, red ▼) One representative out 3 independent titration experiments done in duplicate is shown with the means ± SD indicated. The data of plots (A), (B), (D), (E), and (F) are summarized in S1 Data.