Fig 2. LBK is required for dpp signaling in the Drosophila wing disc.
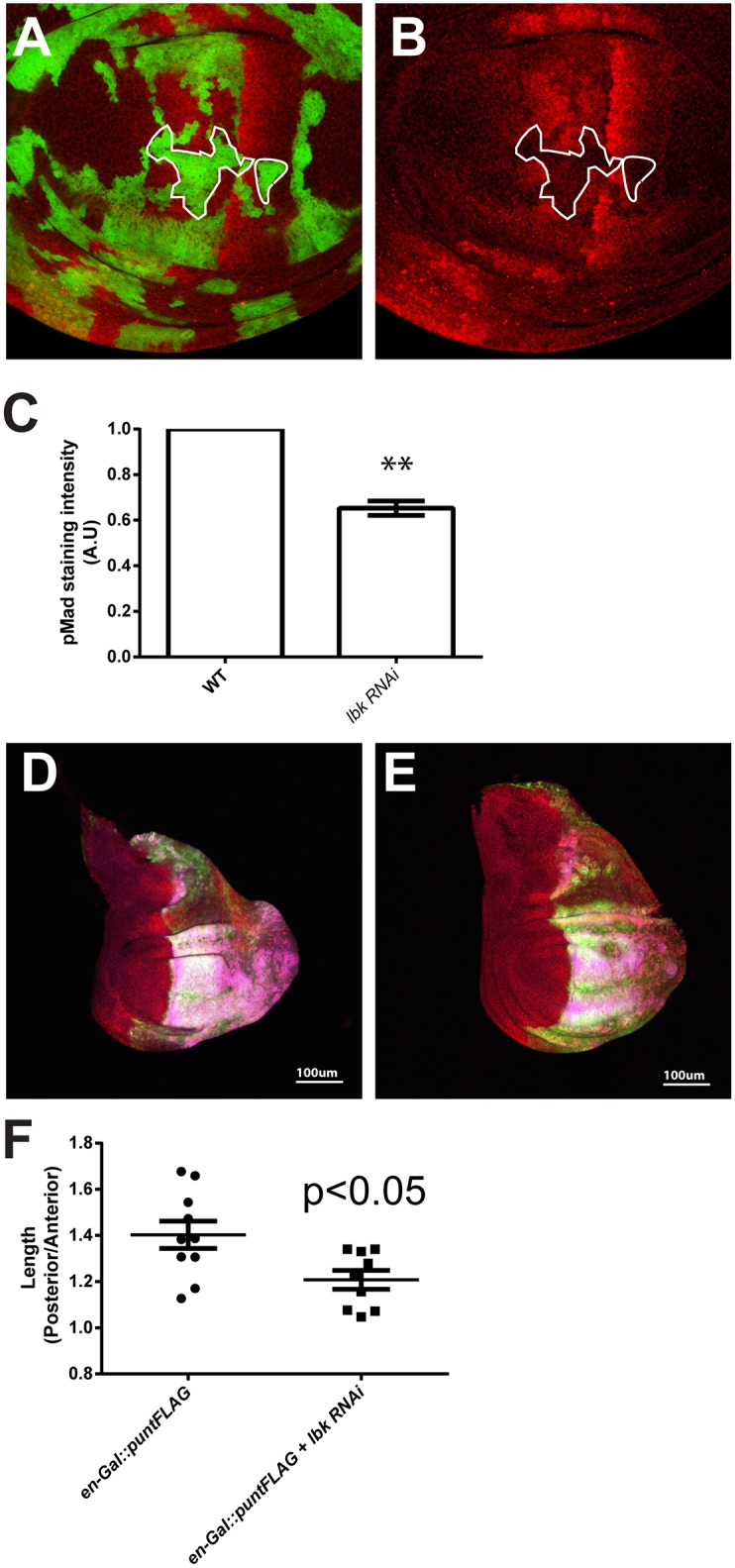
(A, B) Loss of lbk results in reduced phosphorylated MAD (pMAD) levels. RNAi-lbk clones were made with flip-out technology [45]. (A) Green labels clones where lbk is reduced, while red stains for pMad. (B) In RNAi-lbk clones (green), pMAD (red) was significantly decreased (C) compared to the neighboring cells (non-green cells). The genotype of these flies is hs-Flp[122]/+; act>y+>Gal-4 UAS-GFP/UAS-RNAi-lbk. (D) punt (type II receptor) was over expressed in the posterior compartment of the third instar larval wing disc using an en-Gal4 driver. The posterior compartment is labeled by GFP expression (green). punt expression was labeled by its FLAG tag staining (magenta). The genotype of these flies is UAS-Dcr2/+; en-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+; UAS-punt-3xFLAG/+. (E) punt was over expressed while the lbk gene was knocked down in the posterior compartment of the third instar larval wing disc. The posterior compartment was labeled by GFP expression (green). punt expression was labeled by its FLAG tag staining (magenta), and pMad is labeled red. The genotype of these flies is UAS-Dcr2/+; en-Gal4 UAS-GFP/ UAS-RNAi-lbk; UAS-punt-3xFLAG/+. Overexpression of punt caused the enlargement of posterior compartment, but the effect of punt was alleviated by RNAi-lbk. (F) The size of posterior compartment was significantly diminished. The average ratios of diameters of the anterior to posterior compartments are 1.40 and 1.15 (p<0.05) (S2 Table).
