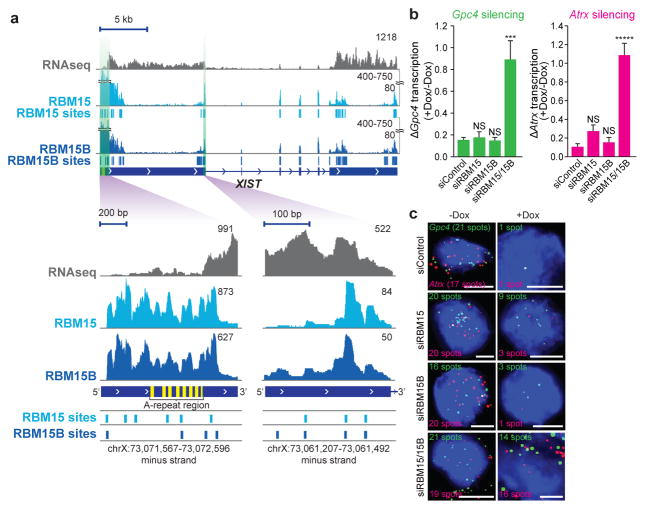
Figure 1. RBM15 and RBM15B are necessary for XIST-mediated gene silencing.
a, RBM15 and RBM15B show similar binding patterns in XIST. Shown is the distribution of normalized RBM15 and RBM15B iCLIP tags (in unique tags per million, uTPM) and statistically significant CITS. Light blue vertical lines, RBM15; dark blue vertical lines, RBM15B; P < 0.0001. b, c, Knockdown of both Rbm15 and Rbm15b (siRBM15/15B) impair XIST-mediated gene silencing. XIST expression was induced by doxycycline, and the X-linked genes Gpc4 (green) and Atrx (red) were quantified by RNA-FISH (b). Representative FISH images are shown with DAPI nuclear counterstain (blue) (c). The number of detected RNA spots for both genes are indicated on each image. Scale bars, 5 μm. Data are mean ± s.e.m. for 50 cells from one experiment. ***P < 0.001, *****P < 0.0001, relative to siControl by unpaired two-sample t-test. NS, not significant.