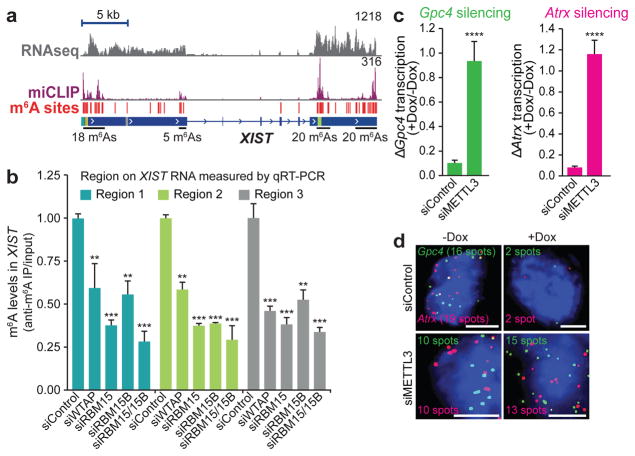
Figure 3. N6-adenosine methylation is necessary for XIST-mediated gene silencing.
a, m6A residues (red lines) identified via miCLIP are broadly distributed along XIST. Normalized miCLIP17 tags are shown in purple. b, Methylation of XIST requires RBM15 and RBM15B. m6A levels in XIST were quantified by m6A-RNA immunoprecipitation followed by qRT–PCR of three m6A regions of XIST. Data are mean ± s.e.m. from six samples coming from three technical replicates of two biological replicates. ***P < 0.0001, **P < 0.001 relative to siControl by unpaired two-sample t-test. c, d, m6A promotes XIST-mediated gene silencing. XIST expression was induced by Dox, and X-linked genes Gpc4 (green) and Atrx (red) were quantified by RNA-FISH (c). Representative FISH images are shown (d). The number of detected RNA spots is indicated on each image. Scale bars, 5 μm. Data are mean ± s.e.m. for 50 cells from one experiment. ****P < 0.005 relative to siControl by an unpaired two-sample t-test.