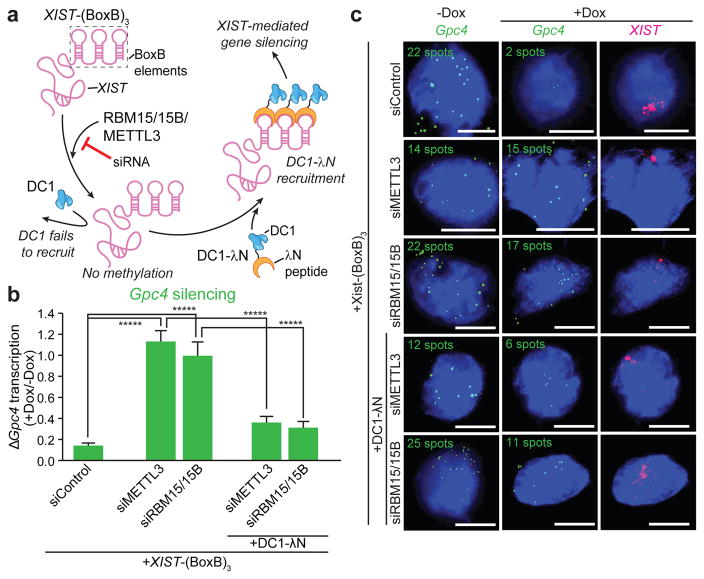
Figure 5. m6A-independent tethering of DC1 to XIST is sufficient to exert XIST-mediated gene silencing.
a, Schematic of tethering approach. The 3′ end of XIST was genomically modified with three BoxB sequences (XIST–(BoxB)3). m6A-dependent recruitment of DC1 is blocked in methylation-deficient cells; however, artificial tethering can be achieved with DC1–λN, which binds to the BoxB elements in XIST–(BoxB)3. b, c, Dox-induced expression of XIST–(BoxB)3 results in gene silencing in siControl-transfected cells, but not in siMETTL3 or siRBM15 and siRBM15B co-transfected cells. DC1–λN rescued silencing in these cells, suggesting that the primary function of m6A in XIST-mediated gene silencing is to recruit DC1 to XIST. Quantification of Gpc4 expression is shown in b. Representative FISH images showing DAPI-stained nuclei (blue), Gpc4 RNA (green), and XIST (pink) are shown in c. Scale bars, 5 μm. Data are mean ± s.e.m. in b for 50 cells from one experiment. *****P < 0.0001 by unpaired two-sample t-test.