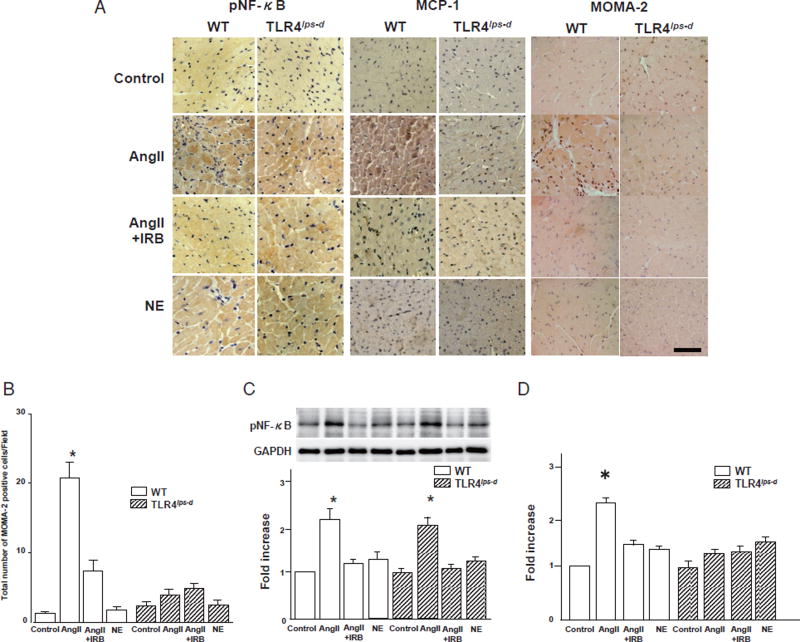
Fig. 3. Expression of pNF-κB and MCP-1 and infiltration of monocytes/macrophages in the heart.
WT, wild-type mice; T1r4lps-d, TLR4-deficient mice; AngII, angiotensin II; NE, norepinephrine; IRB, irbesartan.
A. Immunohistochemical staining for pNF-κB and MCP-1 and infiltration of monocytes/macrophages in the mouse heart tissue. pNF-κB stained brown in the cytoplasm and nuclei in the heart. MCP-1 stained brown in the cytoplasm in the heart. Monocytes/macrophages stained brown in the interstitial regions in the heart. MOMA-2; marker of monocytes/macrophages. Bar, 50 µm.
B. Quantitative analysis of the infiltration of monocytes/macrophages in the heart. Bar, SE. Experiments, AngII-treated WT and T1r4lps-d groups; n= 6, the other groups; n= 3. *P< 0.05 vs. the control, AngII + IRB or NE group in both the WT and T1r4lps-d mice.
C. Results of a quantitative analysis of the expression of pNF-κB in the heart. Bar, SE. Experiments, n=3. *p<0.05 vs. the control, AngII + IRB or NE group in both the WT and T1r4lps-d mice. There were no significant differences in the expression of pNF-κB between the WT AngII group and the T1r4lps-d-AngII groups.
D. Quantitative analysis of the expression of MCP-1 in the heart. Bar, SE. Experiments, n = 3. *p<0.05 vs. the other groups.