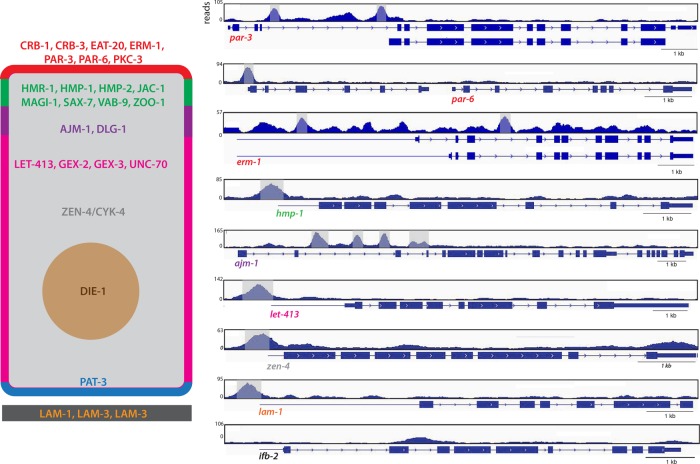
FIGURE 5:
PHA-4 binds to regulatory elements of epithelial factor genes. Left, generic C. elegans epithelial cell, with the apical domain in red, apical junction in green, basal junction in purple, lateral domain in fuschia, basal domain in blue, extracellular matrix in black, cytoplasm in gray, and nucleus in brown. Selected epithelial factors whose regulatory regions are bound by PHA-4 are shown. Right, genome browser displays of PHA-4–binding peaks for a subset of selected genes. Exons are denoted by blue boxes and introns by blue lines with arrowheads. Blue lines preceding the first exon represent untranslated regions. Significant PHA-4 peaks (MACS2; see Materials and Methods) are highlighted in gray. Note that the smaller isoform of par-3 is epithelial specific, suggesting that the large upstream intron in which PHA-4 binds could specifically regulate the expression of this isoform. par-6 is the second gene in an operon, and therefore the binding associated with the upstream gene is also associated with par-6. As a negative control, the midgut specific gene ifb-2 is shown, which lacks PHA-4 binding (bottom).