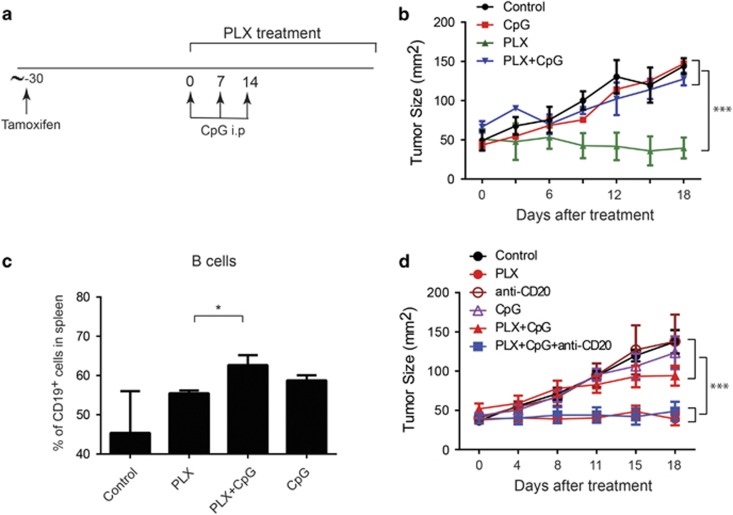
Figure 2.
CpG negates the antitumor activity of BRAF inhibitors in a B-cell-dependent manner. To induce spontaneous melanoma in genetically modified mice, Tyr:CreER; PTENlox/lox; BRAFV600E/+ (BP) mice on a C57BL/6 background (6–8 weeks of age) were treated with 50 mg ml−1 4-hydroxytamoxifen (Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA) to induce the expression of Cre as previously described.23 Mice with measurable tumors received indicated antitumor treatments. (a, b) Tumor-bearing BP mice were treated with daily oral gavage of 100 mg/kg PLX4720 (PLX), intraperitoneal injection of 50 μg CpG once per week for 3 weeks, or both. Tumor growth was monitored every 3 days by measuring the perpendicular diameters of tumors. N=5 mice per group. (c) Single-cell suspensions were prepared from the spleens of tumor-bearing BP mice treated with PLX, CpG or both, and stained with anti-CD4, CD8 and CD19 antibodies (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). The percentages of various immune cell populations (T cells and B cells) in stained samples were analyzed by flow cytometry using a FACSCANTO II cell analyzer (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). CD19+ B cells in spleen in each group were shown. N=5 per group. (d) Tumor-bearing BP mice were simultaneously treated with PLX, CpG or both, as described in (a, b). Also, 50 μg of anti-mouse CD20 Ab IgG2a kindly provided by Biogen Idec (San Diego, CA, USA) were injected intravenously in tumor-bearing BP mice once per week for 2 weeks to deplete B cells either alone or together with PLX and CpG. Isotype control antibody purchased from Sigma were similarly injected as a control. Tumor sizes were monitored every 3 days (Control group: N=7; PLX group: N=6; anti-CD20 group: N=5; CpG group: N=4; PLX+CpG group: N=6; PLX+CpG+anti-CD20 group: N=6). Data expressed as mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001, two-way ANOVA (b, d) or one-way ANOVA (c) plus post hoc Turkey test.