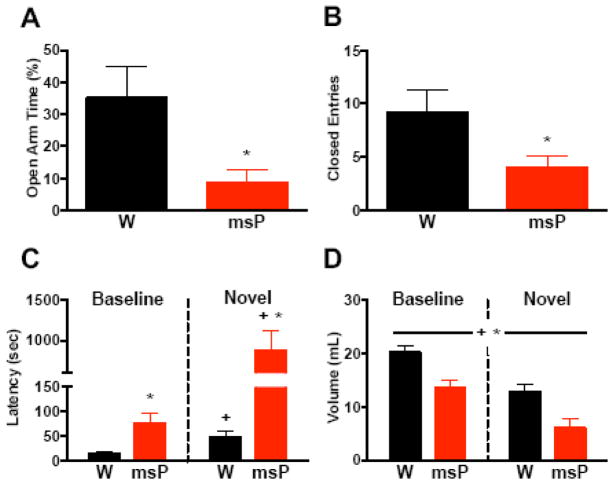
Figure 1. MsP rats display an innate anxiety-like phenotype.
(A) Percentage of time spent on the open arm of the elevated plus maze (EPM) in non-selected Wistar (W, n=5) and msP (n=7) rats. (B) Total entries made into the closed arm of the EPM in rats from A. (C) Latency to drink from a palatable chocolate solution under baseline and novel environments in Wistars (n=9) and msPs (n=11). (D) Total volume of chocolate solution consumed in rats from C. Data expressed as mean ± SEM. Asterisks (*) denote significant genotype differences, whereas plus signs (+) denote significant differences from baseline conditions (p<0.05). A continuous line across groups denotes significant main effects.