Figure 6.
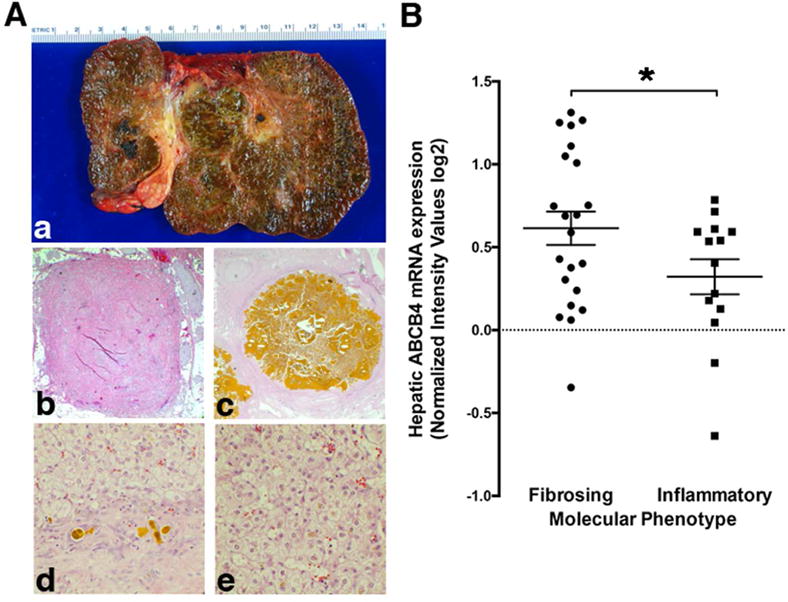
Association between hepatic expression of ABCB4 mRNA and inflammatory molecular signature in infants with EHBA. (Aa), Explanted liver of a 23-month-old-Somalian female with the clinical diagnosis of MDR3 disease, supported by bi-allelic non-synonymous variants in ABCB4. The explant shows biliary cirrhosis as well as (Ab) complete fibrous obliteration of the extrahepatic bile duct, (Ad) bile duct proliferation with bile plugs, (Ac) intrahepatic gallstones, and (Ae) canalicular cholestasis. Decreased hepatic expression of ABCB4 in subjects with a transcriptomic profile of inflammatory EHBA is shown in (B). Hepatic microarray gene expression data from a study on 40 subjects with EHBA identifying molecular signatures for inflammatory and fibrosing phenotypes were mined for the relative expression levels of ABCB4. Unpaired t test was applied to test for statistical differences between the groups with *p<0.05.
