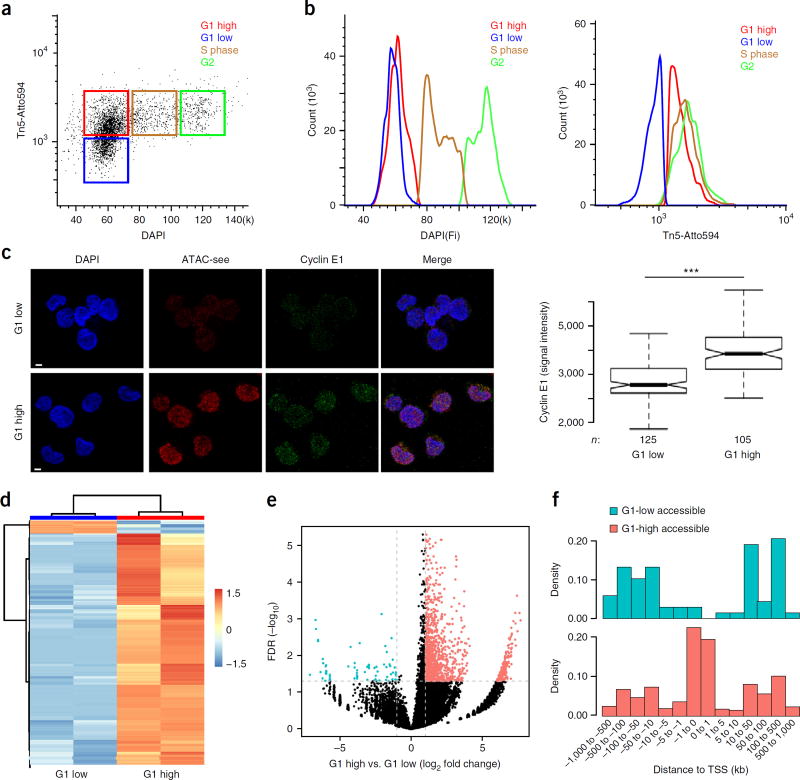
Figure 5.
ATAC-see reveals cell-cycle-specific genome accessibility. (a) Flow cytometry with ATAC-see. Dot plot of signal intensity in dual staining for DAPI and ATAC-see of GM12878 cells; results showed four groups of cells: G1 low, G1 high, S phase, and G2. (b) Quantitation of DAPI (left) and ATAC-see (right) signals from different groups. (c) Cyclin E1 staining in ATAC-see-sorted G1-high and G1-low cells. Left panel, representative images from confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 2 µm. Right panel is a box plot depicting signal intensity measurement. n, cell number; ***, P < 0.001, Student t-test. (d) Heatmap shows cluster of different ATAC-seq accessible regions between the G1-high and G1-low cells (FD > 2, FDR < 0.05); each group has one replicate. (e) The volcano plot represents genome-wide comparisons of accessible regions in G1-high versus G1-low cells. (f) The density histograms represent the distribution of the more accessible regions in G1-high and G1-low cells across the transcription starting sites (TSS). The more accessible regions in the two groups were color coded.