Abstract
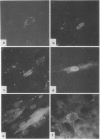
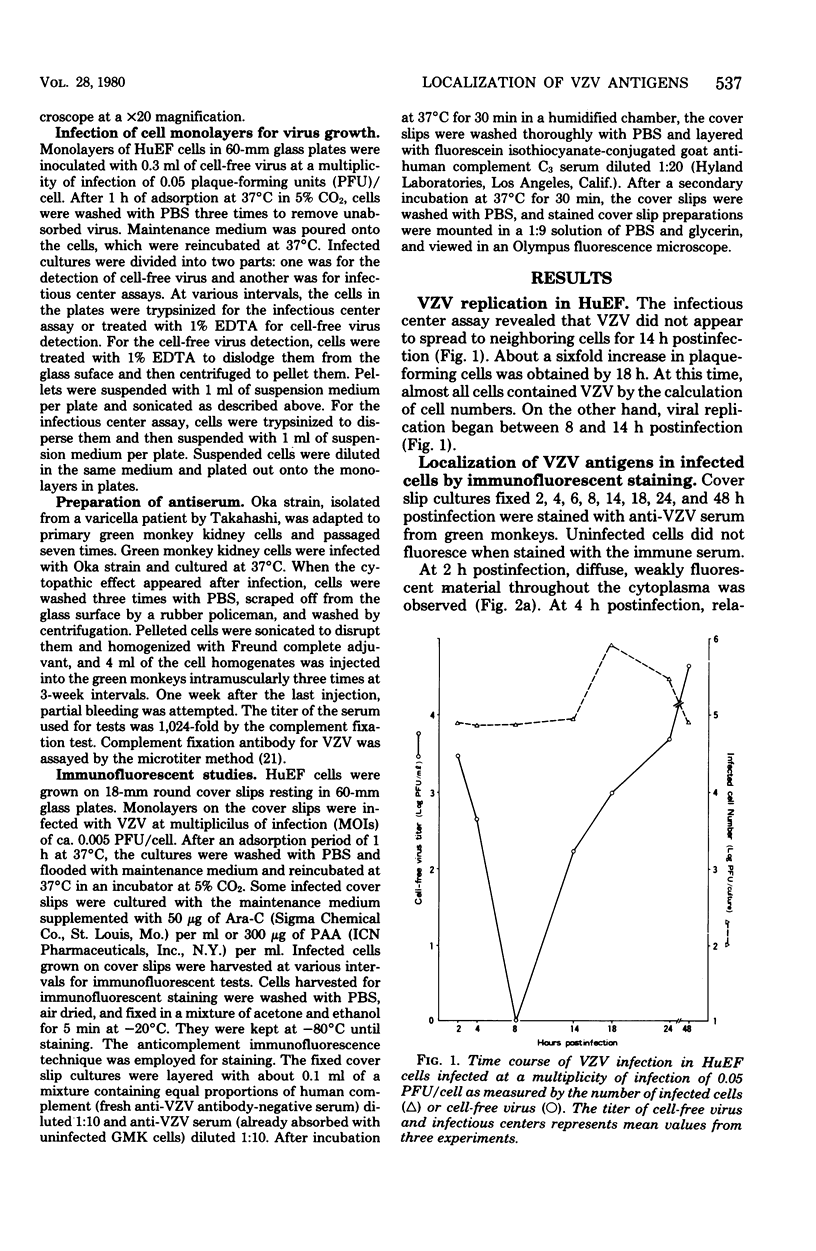
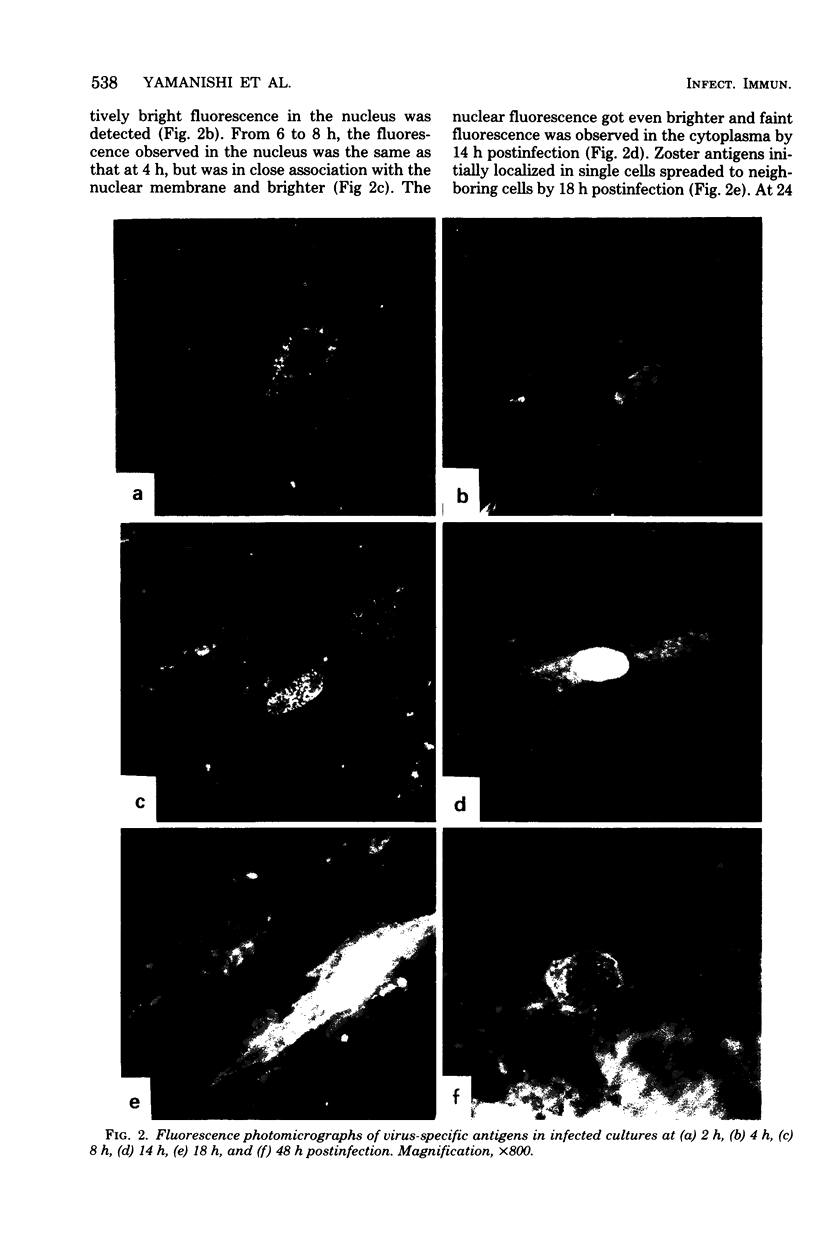
When human embryonic fibroblast cells were infected with cell-free varicella-zoster virus, virus replication began between 8 and 14 h postinfection, and 4 more h werp required for the virus to infect neighboring cells. Virus-specific antigens were traced by the anticomplement immunofluorescent antibody technique. Virus antigen was first detectable 2 h postinfection in the cytoplasma, and diffuse fluorescence was observed in the nucleus as early as 4 h after infection. The nuclear fluorescence got brighter and cytoplasmic fluorescence was observed at 14 h postinfection. The spread of virus to the neighboring cells was recognized in 18 h postinfection. In the period of 24 to 48 h, antigens were seen at the nuclear membrane region and in the cytoplasma. Very strong fluorescence was restricted mainly to the nucleus, when phosphonoacetic acid or cytosine arabinoside was added to the infected cultures and the cells were incubated for 48 h.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Geder L. Evidence for early nuclear antigens in cytomegalovirus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Aug;32(2):315–319. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo G., Beth E., Hämmerling U., Tarro G., Kourilsky F. M. Detection of early antigens in nuclei of cells infected with cytomegalovirus or herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 by anti-complement immunofluorescence, and use of a blocking assay to demonstrate their specificity. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jan;19(1):107–116. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Géder L., Váczi L. Localization of nuclear and cytoplasmic herpes simplex antigens in infected cells by immunofluorescence. Acta Virol. 1968 Mar;12(2):97–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus. IV. Specific inhibition of virus-induced DNA polymerase activity and viral DNA replication by phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1560–1565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1560-1565.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLLER M., GOENCZOEL E., VACZI L. STUDY OF THE MULTIPLICATION OF VARICELLA-ZOSTER VIRUS BY THE FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY TEST. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1963;10:183–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E., Overby L. R. Inhibition of DNA polymerase from herpes simplex virus-infected wi-38 cells by phosphonoacetic Acid. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1281–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1281-1283.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar E. C., Huang Y. S., Huang E. S. Purification and characterization of varicella-zoster virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):249–256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.249-256.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May D. C., Miller M. R., Rapp F. The effect of phosphonoacetic acid on the in vitro replication of varicella-zoster virus. Intervirology. 1977;8(2):83–91. doi: 10.1159/000148882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Rapp F. Varicella-zoster virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):515–524. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F., VANDERSLICE D. SPREAD OF ZOSTER VIRUS IN HUMAN EMBRYONIC LUNG CELLS AND THE INHIBITORY EFFECT OF LODODEOXYURIDINE. Virology. 1964 Mar;22:321–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N., Waruszewski D. T., Armstrong J. A., Atchison R. W., Ho M. Evaluation of anti-complement immunofluorescence test in cytomegalovirus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):633–638. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.633-638.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross L. J., Watson D. H., Wildy P. Development and localization of virus-specific antigens during the multiplication of herpes simplex virus in BHK 21 cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):115–122. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLOTNICK V. B., ROSANOFF E. I. Localization of varicella virus in tissue culture. Virology. 1963 Apr;19:589–592. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Improved yields of cell-free varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):709–715. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.709-715.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., De Harven E. Herpes simplex virus and human cytomegalovirus replication in WI-38 cells. I. Sequence of viral replication. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):919–930. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.919-930.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The T. H., Klein G., Langenhuysen M. M. Antibody reactions to virus-specific early antigens (EA) in patients with cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jan;16(1):1-7,9-12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váczi L., Gönczöl E. The effect of cytosine-arabinoside on the multiplication of cytomegalovirus and on the formation of virus-induced intracellular antigens. Acta Virol. 1973 May;17(3):189–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER T. H., COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody studies with agents of varicella and herpes zoster propagated in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Aug-Sep;86(4):789–794. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Stevens J. G. Effect of cytosine arabinoside on viral-specific protein synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.71-80.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Ogino S., Asano Y., Otsuka T., Takahashi M., Baba K., Yabuuchi H. Comparison of 4 serological tests--complement fixation, neutralization, fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen and immune adherence hemagglutination--for assay of antibody to varicella-zoster (V-Z) virus. Biken J. 1979 Jun;22(2):55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]