Figure 2.
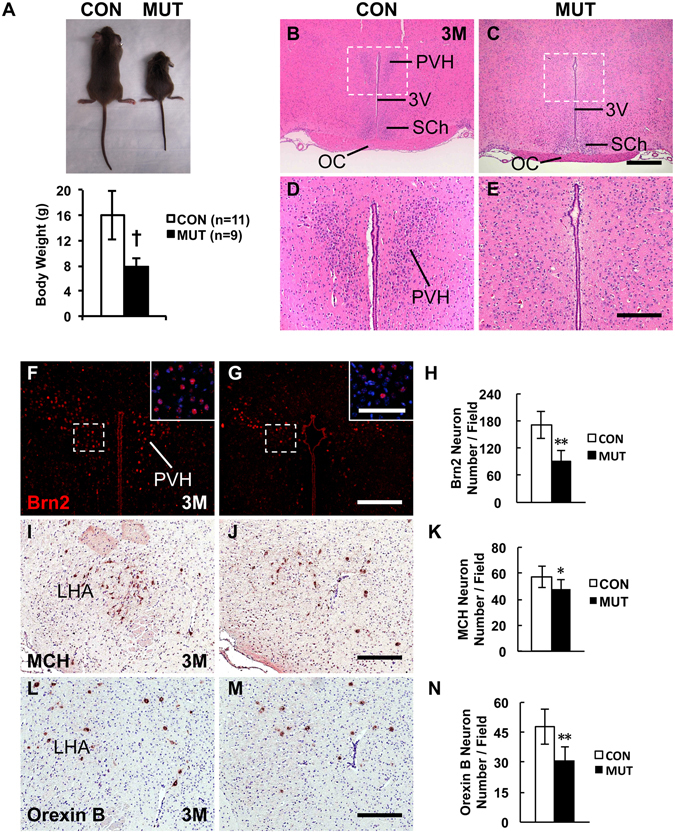
Adult COUP-TFII gene mutant mice with RXCre display growth retardation and compromised PVH nucleus. (A) Body weight of the RXCre/+; COUP-TFIIF/F male mutant mice (n = 6) is approximately half of that of the control (n = 8) at wean. The H&E staining data reveal that compared with the control (B,D), the PVH nucleus is barely detectable in the mutant at 3 M (C,E). (D,E) Inserts in (B,C). Compared with the control (F), there are very few Brn2+ PVH neurons in the mutant at 3 M (G and insert), and the reduction is significant (H and insert). Compared with the control (I), there are fewer MCH neurons in the mutant LHA region at 3 M (J), and the reduction is significant (K). Compared with the control (L), there are fewer Orexin B neurons in the mutant LHA region at 3 M (M), and the reduction is significant (N). 3 V, third ventricle; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; OC, optic chiasm; PVH, paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus; SCh, suprachiasmatic nucleus. The quantitative data in (H,K and N) were generated from the analysis of three pairs of control and mutant mice. The data indicate the mean ± SD. Student’s t-test, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; †P < 0.001. Scale bars, (B,C) 500 μm; (D,E,F,G) 200 μm; inserts of (F,G) 100 μm; (I,J,L,M) 100 μm.
