Figure 5.
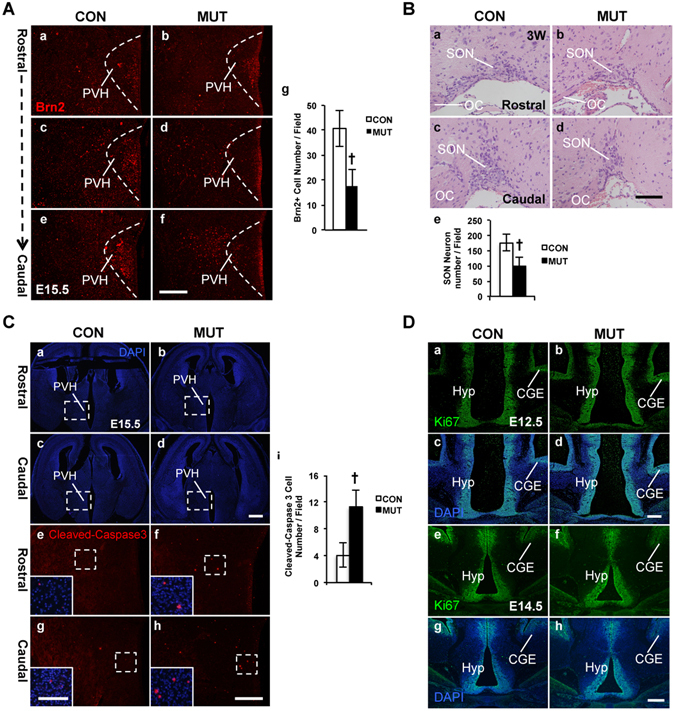
Reduction of the Brn2+ early differentiating PVH neurons, hypocellular SON nucleus, and increased apoptosis in the COUP-TFII mutant. (A) Brn2+ early differentiating PVH neurons are reduced in the mutant embryo. Compared with the control (Aa–c), there are much fewer Brn2+ early differentiating PVH neurons along the rostro-caudal axis in the mutant at E15.5 (Ad–f), and the reduction is significant (Ag). The data are collected from three pairs of control and mutant embryos. (B) Development of the SON nucleus is abnormal in the adult mutant mouse. The H&E staining data show that compared with the control (Ba,b), there are much fewer SON neurons in the COUP-TFII mutant (Bc,d). The reduction of magnocellular SON neurons is significant in the mutant (Be). (Ca–h) Increased apoptosis is detected in the COUP-TFII mutant embryo. DAPI staining images of coronal sections with PVH region in the control (Ca,c) and the mutant (Cb,d) at E15.5. Compared with the control (Ce,g and inserts), there are more cleaved-Caspase-3 signals in the mutant PVH region at E15.5 (Cf,h and inserts), and the increase of the cleaved-Caspase-3 signals is significant (Ci). (Da–h) Proliferation is not affected in the COUP-TFII mutant. The expression of Ki67 is comparable between the control (Da,c) and mutant (Db,d) at E12.5. Expression of Ki67 is comparable between the control (De,g) and mutant (Df,h) at E14.5. CGE, caudal ganglionic eminence; OC, optic chiasm; PVH, paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus; SON, supraoptic nucleus. At least three pairs of the control and the mutant mice were used in each study. The data indicate the mean ± SD. Student’s t-test, †P < 0.001. Scale bars, (Aa–f) 200 μm; (Ba–d) 100 μm; (Ca–d) 500 μm; (Ce–h,Da–h) 100 μm; inserts of (Ce–h) 50 μm.
