Figure 3.
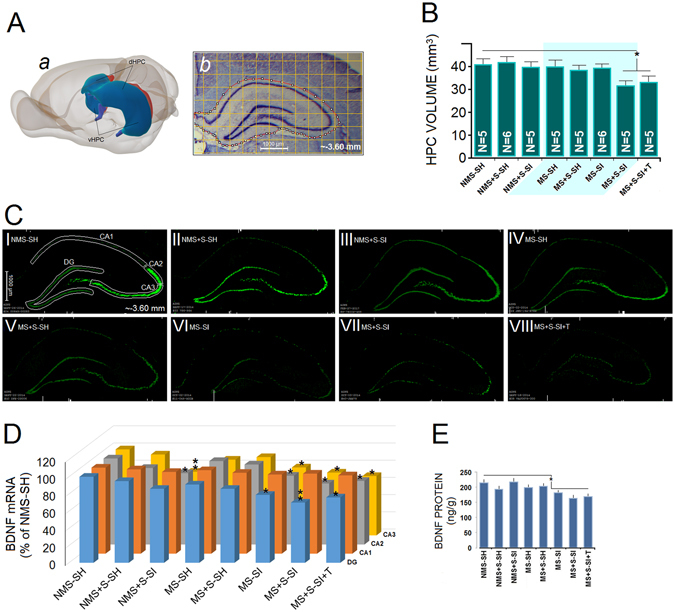
Combined ancestral and adulthood stress reduce hippocampal volume and BDNF expression. (A) A set of 10–11 cross sections of whole hippocampus (AP: −1.4 mm −6.80 mm) were considered for volumetric analysis. (a) 3D reconstruction of the dorsal and ventral hippocampus (blue) in the rat brain. (b) Coronal view of a left dorsal hippocampus illustrating the area that was considered for hippocampal volumetrics. (B) The MS + S-SI and MS + S-SI + T animals indicated decreased HPC volume when compared with other groups. (C) Subpanels I-VIII: The investigated anatomical subregions are delineated for NMS-SH animals. Autoradiographs (unsharp mask-HK1-RSZII2.60 filter-Green) of BDNF mRNA in the dHPC (CA1, CA2, CA3, and DG) indicated that only social isolation reduced BDNF mRNA expression in CA2, CA3 and DG in multigenerationally stressed animals. (D) Density of BDNF mRNA signal in CA1, CA2, CA3 and DG. BDNF mRNA data (N = 3–4 per group) in this experiment are represented as percent of the NMS-SH group; (E) BDNF protein levels in dHPC. No difference was observed between right and left dHPC in terms of BDNF mRNA expression and proteins. Asterisks indicate significant differences: *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01; ANOVA. Error bars show ± SEM.
