Figure 1.
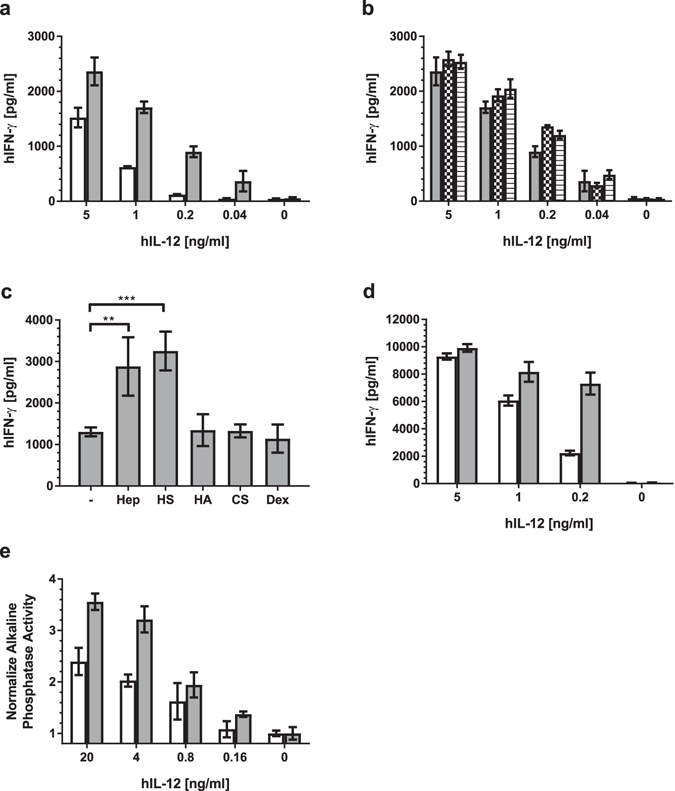
Effect of heparin and other GAGs on hIL-12 bioactivity. (a) hIFN-γ production by NK-92MI cells when incubated with media containing hIL-12 alone (white bars) or with 10 µg/ml heparin (gray bars) was quantified using ELISA. Heparin significantly enhanced hIL-12 bioactivity (p < 0.0001 vs. hIL-12 alone via two-way ANOVA) (b) hIFN-γ production by NK-92MI cells when heparin (10 µg/ml) was added to NK-92MI cells at the same time as hIL-12 (gray bars), 30 mins prior to hIL-12 (checkered bars) or 30 mins after hIL-12 (horizontal). The order of heparin addition had no significant effect on hIL-12 activity (p > 0.05 for all comparisons within each hIL-12 concentration via two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc correction). (c) hIFN-γ production by NK-92MI cells cultured in media containing 200 ng/ml hIL-12 alone (−) or with heparin (Hep), heparin sulfate (HS), hyaluronic acid (HA), chondroitin sulfate (CS), or dextran (Dex) at 10 µg/ml was quantified using ELISA. Asterisks indicate a significant difference between indicated groups (*=p < 0.01 and ***=p < 0.001 via one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc correction). (d) hIFN-γ production by PBMCs when incubated with media containing hIL-12 alone (white bars) or with 10 µg/ml heparin (gray bars) was quantified using ELISA. Heparin significantly enhanced hIL-12 bioactivity (p < 0.0001 vs. hIL-12 alone via two-way ANOVA). (e) Alkaline phosphate activity by HEK-Blue™ IL-12 cells in response to incubation with media containing hIL-12 alone (white bars) or with 10 µg/ml heparin (gray bars) was determined in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions. Heparin significantly enhanced hIL-12 bioactivity (p < 0.0001 vs. hIL-12 alone via two-way ANOVA). All data are represented as mean ± standard deviation from triplicate samples. All experiments were repeated at least twice with similar results.
