Figure 2.
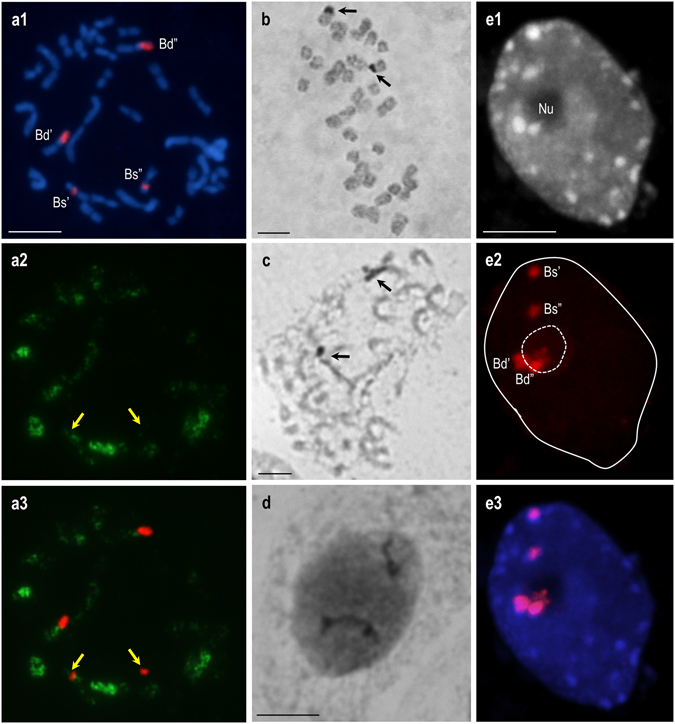
Impact of DNA hypomethylation caused by 0.1 mmol/L 5-AzaC on the preferential inactivation of 35S rRNA genes in the metaphase plates (a1–a3; c) and nuclei (d; e1–e3) of B. hybridum (genotype ABR113). The 5-AzaC treatment changed neither the number of silver-stained loci, nor the non-nucleolar position of B. stacei-inherited 35S rDNA loci. (a1) FISH with 25S rDNA (red fluorescence) as a probe in the mitotic metaphase chromosomes. (a2) 5-MeC foci distribution in the metaphase spread shown on (a1). (a3) Superimposed images of 25S rDNA FISH signals and anti-5-MeC signals. B. stacei-inherited loci are highlighted by yellow arrows. (b–d) The activity of 18S-5.8S-25S rDNA loci in the control (i.e. not treated with 5-AzaC) root-tip cells (b) and after 0.1 mmol/L 5-AzaC treatment in the metaphase plate (c) and interphase nucleus (d). The Ag-NOR bands are highlighted by black arrows. (e1) DAPI counterstained nucleus. (e2) 25S rDNA hybridisation signals (red fluorescence). (e3) Superimposed images of 25S rDNA FISH signals and counterstained chromatin. Nu–nucleolus. Scale bar: 5 µm.
