Figure 5.
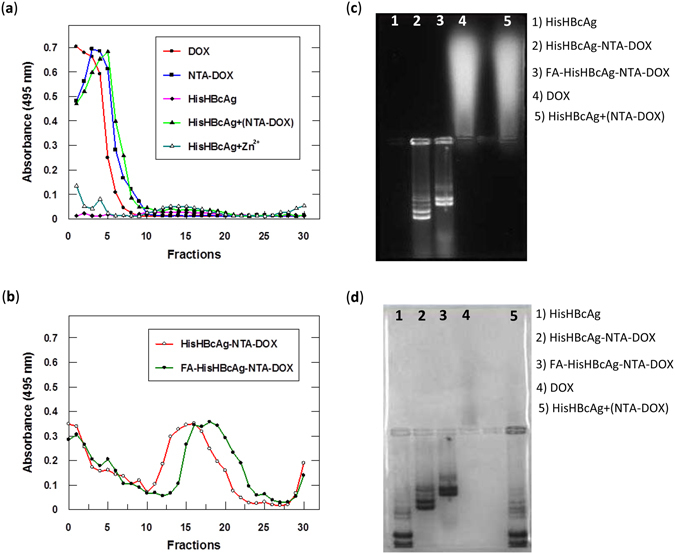
Identification of doxorubicin immobilised on His-tagged VLNPs. (a and b) Doxorubicin (DOX) was detected by measuring absorbance at 495 nm of the fractions obtained from sucrose gradients. (a) DOX, NTA-DOX, HisHBcAg nanoparticles incubated with NTA-DOX in the absence of Zn2+ [HisHBcAg + (NTA-DOX)] stayed on top of the sucrose gradients after centrifugation. HisHBcAg nanoparticles (HisHBcAg) were not detected at A495. HisHBcAg nanoparticles incubated with Zn2+ (HisHBcAg + Zn2+) showed a negligible absorbance at 495 nm. (b) HisHBcAg nanoparticles conjugated non-covalently with NTA-DOX (HisHBcAg-NTA-DOX) and HisHBcAg nanoparticles conjugated covalently with folic acid (FA) and non-covalently with NTA-DOX (FA-HisHBcAg-NTA-DOX) migrated into the sucrose gradient, and the immobilised DOX was detected with A495. (c and d) Native agarose gel electrophoresis of the HisHBcAg nanoparticles conjugated non-covalently with DOX. The same gel was visualised under (c) ultraviolet (UV) illumination, and (d) stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB).
