Figure 7.
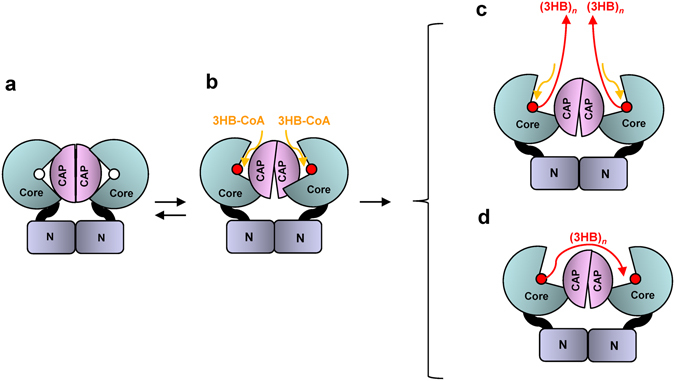
A model of PhaC activation in dimeric form. (a) The closed form as observed in our PhaCCs-CAT structure. The N domain is proposed to contribute to stabilization of the dimer. (b) The partially open form as observed in the PhaCCn-CAT structure. The structure provides a possible path to the active site, but no apparent path for product. (c) The single active site provides a full active site architecture for initiation of acylation and chain elongation. (d) The Cys-bound product in one protomer attacks the 3HB-Cys thioester of the other protomer in the dimer for chain elongation.
