Figure 3.
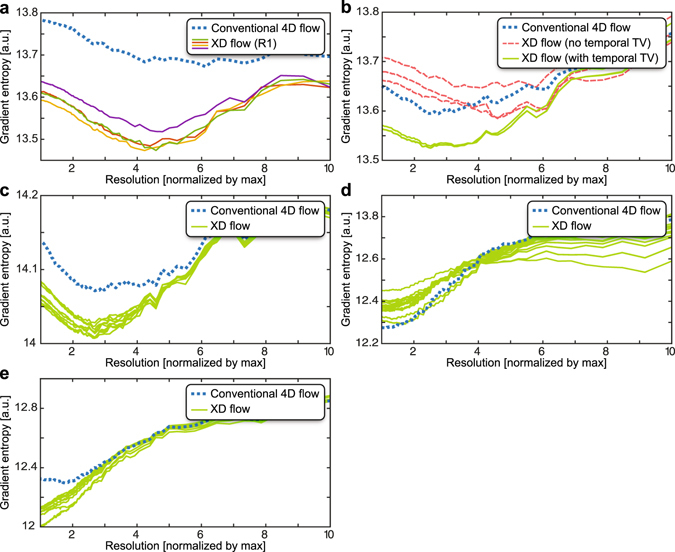
Image sharpness computed using the gradient entropy metric49 (lower values means sharper images). The spatial resolutions of the final reconstructed images were retrospectively lowered, and this metric was computed as a function of image resolution. In the plots, the resolution is normalized by the maximum resolution — 1 corresponds to the acquired spatial resolution, 2 corresponds to 2x lower spatial resolutions, and so on. The true underlying spatial resolution can be considered as the minimum of the curve. This analysis was performed for each XD flow dataset (green or with corresponding colors of the associated figure) and was compared to the original conventional 4D flow reconstruction (dotted blue): (a) subject #1 (Fig. 2) (b) subject #2 (Fig. 4) (c) subject #3 (Fig. 5) (d) subject #4 (Fig. 6), and (e) subject #5 (Fig. 7). Compared to conventional 4D flow, sharper images was observed for XD flow that was able to resolve bulk patient motion as plotted in (a). In other situations, XD flow resulted in lower image resolutions when resolving high-temporal resolution dynamics compared to conventional 4D flow as plotted in (d).
