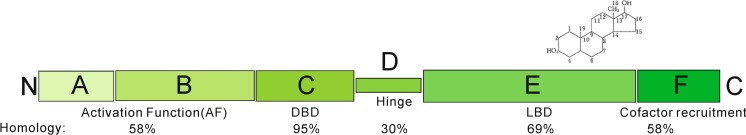
Fig. 1.
Primary structure of the classic estrogen receptors (ER). ERα and ERβ share a common structure with six functional domains (A/B, C, D, E, and F). Domain A/B plays a role in protein-protein interactions and the transcriptional activation of target gene expression. Domain C is responsible for DNA binding and ER dimerization. Domain D, which is a hinge domain linking domains C and E, is involved in the nuclear localization of ERs. Domain E is the ligand-binding domain. Domain F contains cofactor recruitment regions. The similar structures of the receptors both contain a highly homologous DNA-binding region (95 %) and a hormone-binding region with weaker homology(69 %). However, the carboxy- and amino-terminal regions have the least homology (58 %)