Figure 2. Diagram of the relevant PIP2 pathways.
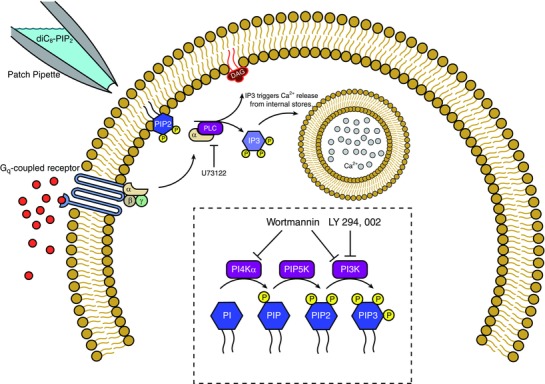
Upon stimulation of Gq‐coupled receptors, the α component of the G‐protein activates phospholipase‐C (PLC), which cleaves membrane‐bound PIP2 into diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol trisphosphate (IP3). DAG activates protein kinase C while IP3 triggers release of Ca2+ ions from internal Ca2+ stores. U73122 blocks the activity of PLC. PIP2 has been demonstrated to modulate several ion channels in previous studies, such as Kv7 channels (Suh & Hille, 2007) and SK channels (Zhang et al. 2014). Inset, the dashed box displays the pathway for production of different PIP molecules (blue hexagons), and the enzymes that phosphorylate each of them (purple boxes). Wortmannin blocks synthesis of PIP2 and PIP3 production while LY294,002 only blocks PIP3 production. Both work by blocking the synthetic enzymes.
