Figure 6. Blockade of glutamate transporter activity evokes a faster firing discharge in RVH rats.
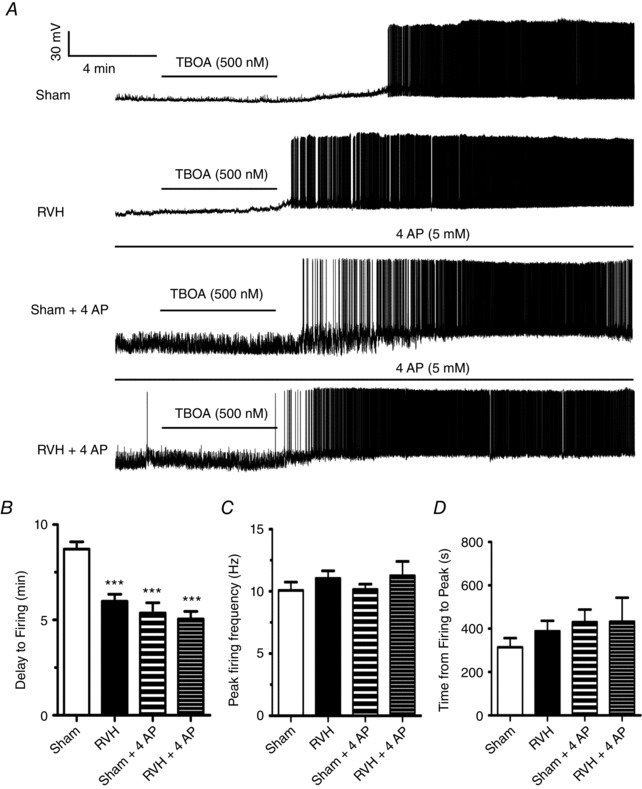
A, representative traces from MNCs from sham and RVH rats showing responses to the glutamate transporter blocker TF‐TBOA (500 nm) in the presence or absence of the I A blocker 4AP (5 mm). TF‐TBOA induced membrane depolarization and evoked firing discharge in all cases. Note, however, that the TF‐TBOA‐evoked firing in the RVH rat occurred with a smaller delay, and that in the presence of 4AP all responses were equalized. B, summary data of mean delay to firing after TF‐TBOA application in MNCs from sham and RVH rats in control ACSF (n = 17 and 19, respectively) and in 4AP (n = 10 and 10, respectively). C, summary data of the mean peak firing evoked by TF‐TBOA in MNCs from sham and RVH rats in control ACSF or in 4AP. D, summary data of the mean time from spike initiation to peak firing evoked by TF‐TBOA in MNCs from sham and RVH rats in control ACSF or in 4AP. *** P < 0.001 vs. sham.
