Figure 2. Inhibition of XE activity by a model nascent leading strand is overcome by the addition of RPA .
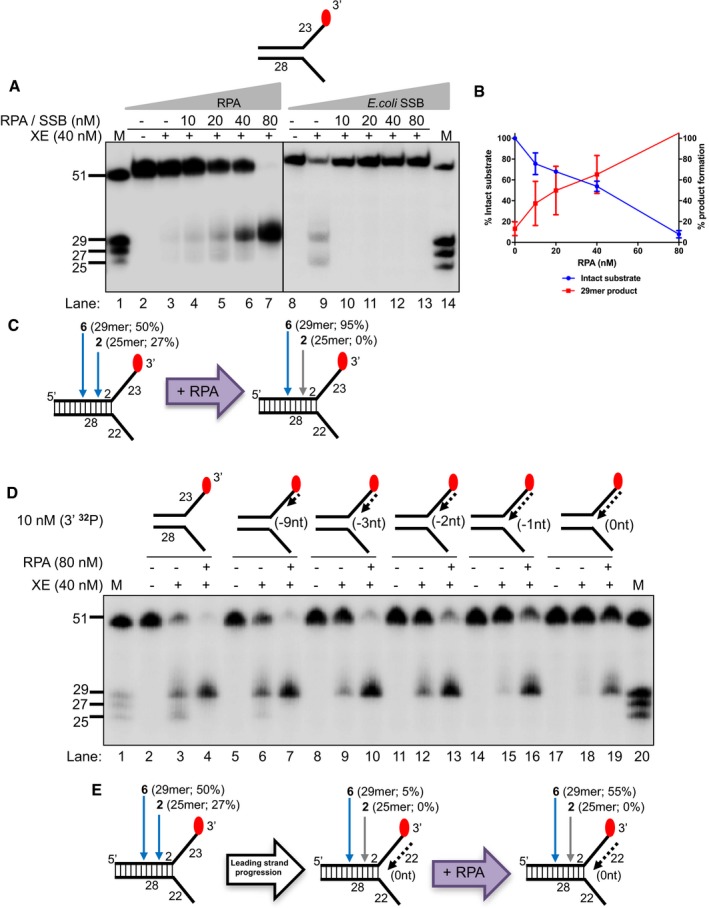
- Nuclease activity of XE on a “simple fork” with increasing concentration of RPA or SSB (Escherichia coli).
- Quantification of intact substrate and incision products as a percentage of initial substrate as in (A). Error bars represent SEM, n = 3.
- A schematic representation of 40 nM XE activity on a “simple fork” in the absence (left) or presence (right) of 80 nM RPA.
- Nuclease activity of XE on fork substrates with increasing length of a model nascent leading strand (simple fork; −9; −3; −2; −1; 0 nt from the fork junction) in the presence or absence of 80 nM RPA.
- A schematic representation of XE activity in the presence and absence of RPA as in (D).
