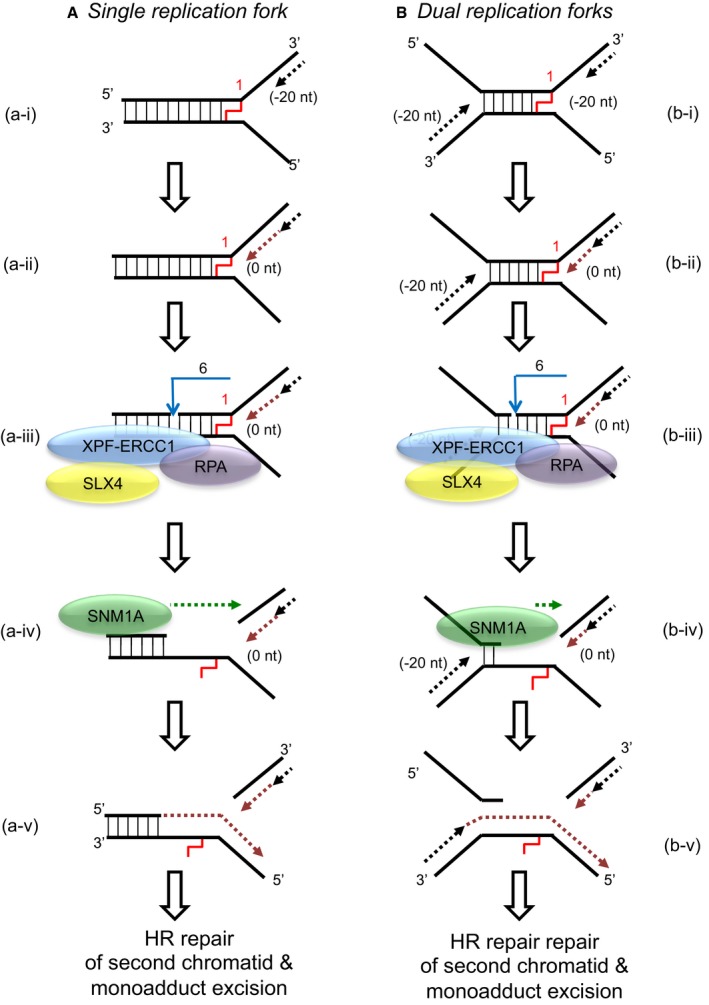
In the event of dual replication fork convergence onto an ICL, both nascent leading strands initially stall ˜20–40 nt from the ICL (step b‐i). CMG complexes from both replication forks unload from both leading strands, as previously described (Long
et al,
2014; Zhang
et al,
2015) which enables one nascent leading strand to gradually progresses to 1 nt from the ICL (“0” position; step b‐ii) as previously described (Raschle
et al,
2008; Zhang
et al,
2015). The structure that arises at this stage is inhibitory for XPF‐ERCC1. However, in the presence of RPA, XPF‐ERCC1 will be able to incise the structure (on the lagging‐strand template associated with the fork which has progressed to 0 nt) within the duplex region, 6 nt from the ICL (step b‐iv). This XPF‐ERCC1‐RPA‐induced incision enables SNM1A to load onto and digest past the ICL (step b‐v). The net result of XPF‐ERCC1‐RPA‐SNM1A is ICL unhooking, which enable the translesion (TLS) synthesis step, where the strand extended by the TLS polymerase is the nascent leading strand which remained arrested at ˜20–40 nt from the ICL on the second converged fork and did not strike the ICL (step b‐vi). Homologous recombination‐based repair of the broken chromatid completes repair and facilitates fork restart.