Figure 6. Overview of hibernation modes across bacteria.
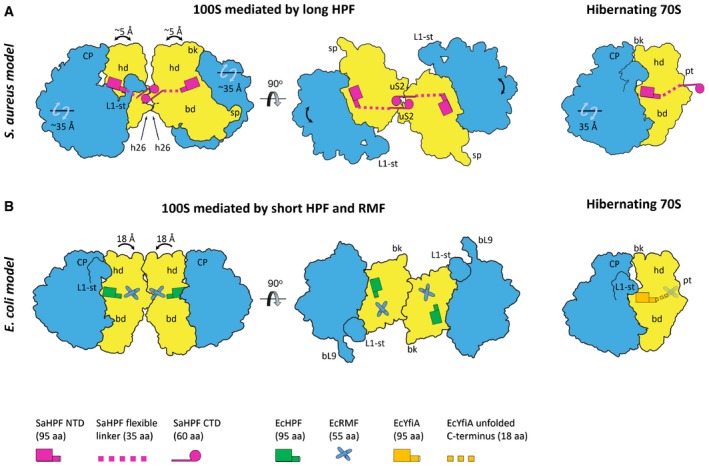
- Ribosome hibernation in Staphylococcus aureus occurs upon binding of SaHPF‐NTD to the SSU, while dimerization is mediated by interactions of SaHPF‐CTDs. Secondary contacts involve helix 26. Relative rotations of the subunits and head movements are indicated in this panel and panel (B).
- Ribosome hibernation in Escherichia coli involves three proteins. Simultaneous binding of EcRMF and EcHPF leads to the conformational change in the head of the SSU, which in turn allows two ribosomes to interact via contacts between ribosomal proteins and rRNA (Kato et al, 2010; Ortiz et al, 2010). Hibernation can also occur upon binding to the YfiA protein, which prevents binding of EcRMF due to its extended C‐terminal tail, thereby not promoting dimer formation (Polikanov et al, 2012).
