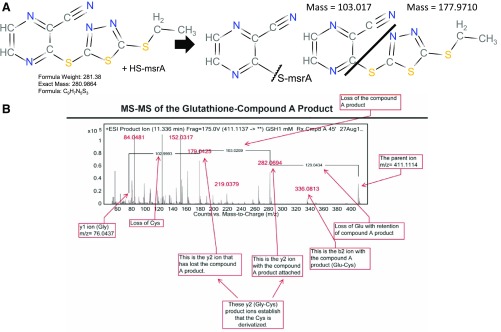
Fig. 5.
MS analysis of msrA– and glutathione–compound A adducts. (A) Scheme for the reaction of the single cysteine residue on msrA with compound A. The major modified form of msrA gained +103.0 Da in mass, consistent with addition of the cyanopyrazine ring from compound A to the free cysteine of msrA. (B) Tandem mass spectrum of the glutathione cysteine reaction product demonstrates a cyanopyrazine ring. A molar excess of glutathione reacted readily with compound A to form a derivative with a monoisotopic mass of 410.1021 and another product of mass 177.9710, which has the same mass as compound A less the cyanopyrazine moiety [see (A)]. Boxes indicate the position of various mass fragment ions from the reaction. ESI, electrospray ionization; HS-msrA; mutated msrA with a single sulfydryl group.