Figure 2.
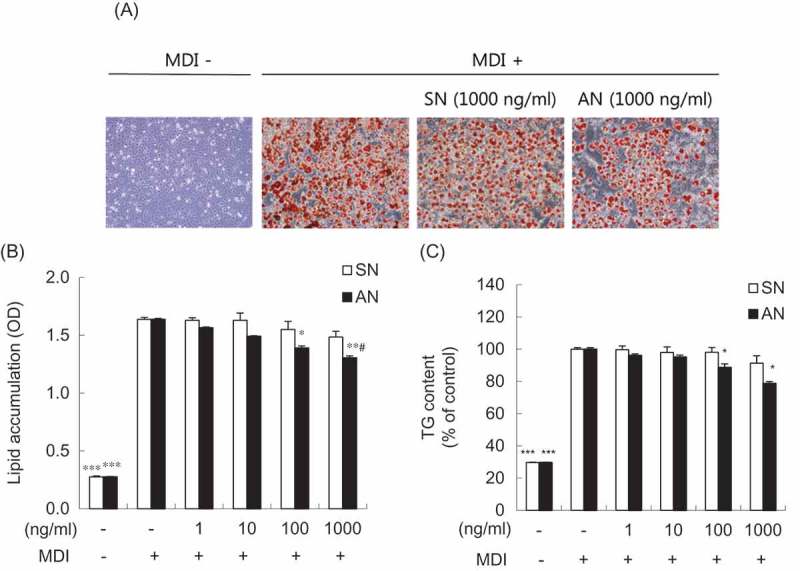
Effects of single-layer nanoemulsion (SN) and alginate double-layer nanoemulsion (AN) on the lipid accumulation and triglyceride (TG) content in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. (a) The effect of SN and AN on lipid droplet formation was measured by Oil Red O staining. Differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes were treated with 1000 ng/mL of SN or AN for 24 h. Representative cell images were captured at 100× magnification. MDI, differentiation medium containing 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine, dexamethasone, and insulin. Quantification of (b) intracellular lipid accumulation and (c) TG content. Differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes were treated with 0 (MDI treated control), 1, 10, 100, or 1000 ng/mL of SN or AN for 24 h. Oil Red O-stained lipids were extracted in absolute isopropanol, after which the absorbance of the solution was measured at 520 nm. TG content was determined using enzymic colorimetric methods. OD, optical density. Data are expressed as the mean ± SE of at least three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate (n = 3). One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison tests: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared with MDI treated control group. Student’s t test: #p < 0.05 compared with SN group.
