Figure 3. Hematopoiesis Is Composed of Dissimilar Clones with Cell-Autonomous Behavior.
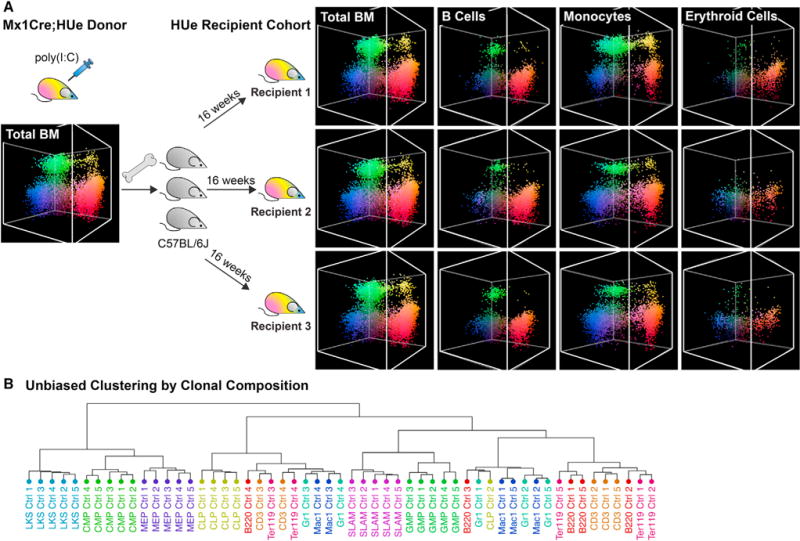
(A) The HUe recipient cohort—a cohort of mice with highly similar clonal fluorescence pattern. To generate a recipient cohort, Mx1-Cre;HUe mice induced with pIpC were used as donors. Randomly labeled fluorescent bone marrow cells from multiple Mx1-Cre;HUe donors were pooled as one mixture and isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Fluorescent HSPCs (LineageLoSca+cKit+) mixed with support cells from C57BL/6J were transplanted into each of 20 lethally irradiated C57BL/6J recipients. After 16 weeks of reconstitution, the recipients showed high consistency in clonal output including proliferation, fluorescence, and lineage characteristics in all hierarchy of hematopoietic cell types. HUe clonal fluorescent patterns of B cells, monocytes, and erythroid cells in multiple recipients are shown, illustrating consistency among the recipients and the distinction between different cell compartments.
(B) Unbiased hierarchical clustering of HUe fluorescence profiles. The distribution of HUe fluorescence in each hematopoietic cell type (e.g., B cells in Figure 1G) represents the clonal composition of that cell type in each mouse (Ctrl 1-5). Hierarchical clustering of such HUe profiles is shown. The clustering groups the same cell type samples from different mice together, illustrating that the pronounced pattern of proliferation and lineage bias exhibited by the individual clones is sufficient to consistently distinguish individual cell types from multiple recipients based on their clonal composition.
See also Figures S4 and S5.
