Fig. 6.
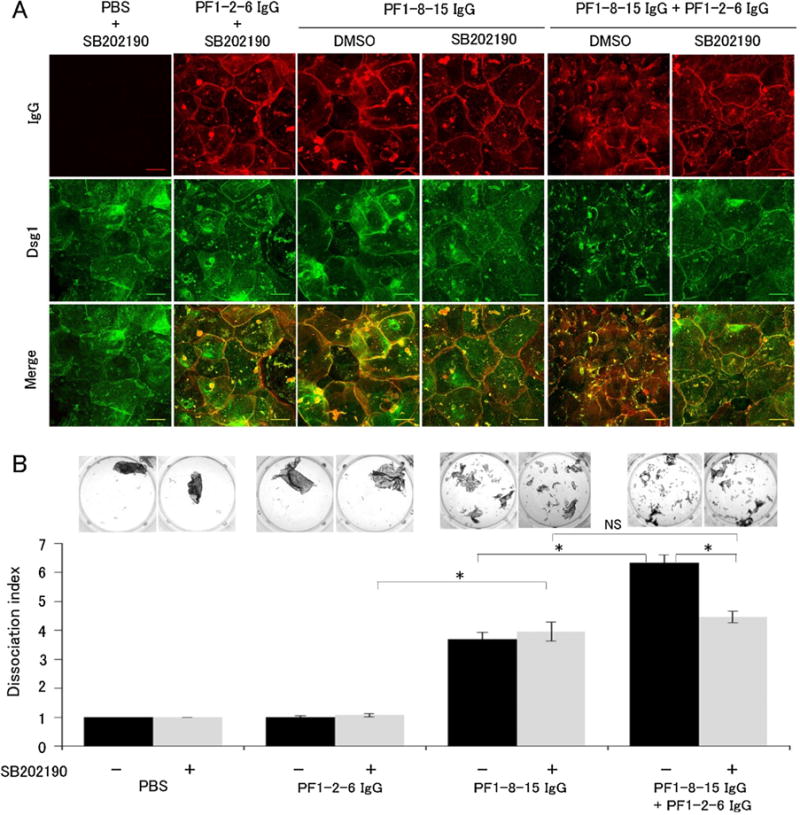
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK) inhibition prevented anti-desmoglein 1 (Dsg1) IgG monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) Dsg1 clustering, but not loss of cell adhesion in vitro. A: Immunofluorescence imaging of primary keratinocytes with the p38MAPK inhibitor SB202190. Cells were pre-incubated with SB202190 for 1.5 h followed by co-incubated with anit-Dsg1 IgG mAbs and SB202190 for 24 h. SB202190 prevented Dsg1 clustering induced by the mixture of PF1-8-15 IgG and PF1-2-6 IgG in cultured primary keratinocytes. Bar = 50 μm. B: Dissociation assay with SB202190 corresponding to the immunofluorescence imaging series (n = 6 per group). SB202190 failed to prevent loss of cell adhesion in keratinocytes incubated with the single PF1-8-15 IgG. On the other hand, SB202190 partially suppressed loss of cell adhesion in keratinocytes incubated with the mixture of PF1-8-15 IgG and PF1-2-6 IgG. Dissociation index of the single PF1-8-15 IgG with SB202190 was almost the same as that of the mixture of PF1-8-15 IgG and PF1-2-6 IgG with SB202190. Photos show the fragments condition of each well. Data are mean SEM. *p < 0.05. NS, not significant.
