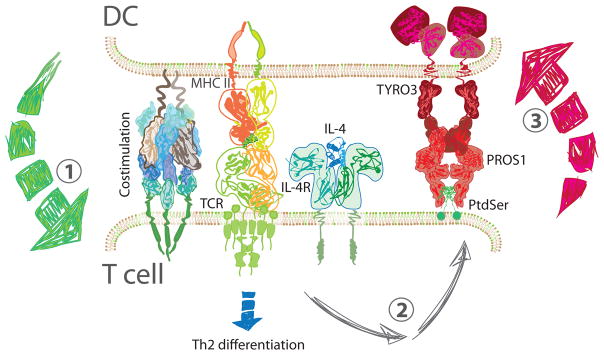
Figure 2. Regulation at the Immune Synapse.
CD4+ T cells are activated and begin to differentiate in response to three signals (1). DCs present peptide antigen on the MHC class II and provide costimulation as well, to ensure productive signaling. Cytokines direct differentiation to specific CD4+ T helper subsets; here IL-4 leads to Th2 differentiation. In addition, the combination of TCR and IL-4 signaling in T cells leads to the upregulation of PROS1 on their surface (2). In turn, PROS1 interacts with TYRO3 on the DC and engages a negative feedback mechanism that limits DC activation (3). Abbreviations: DC, dendritic cell; IL-4, interleukin 4; IL-4R, interleukin 4 receptor; MCH II, class II major histocompatibility complex; PROS1, Protein S; PtdSer, phosphatidylserine; TCR, T cell receptor; Th2, type 2 helper T cell.