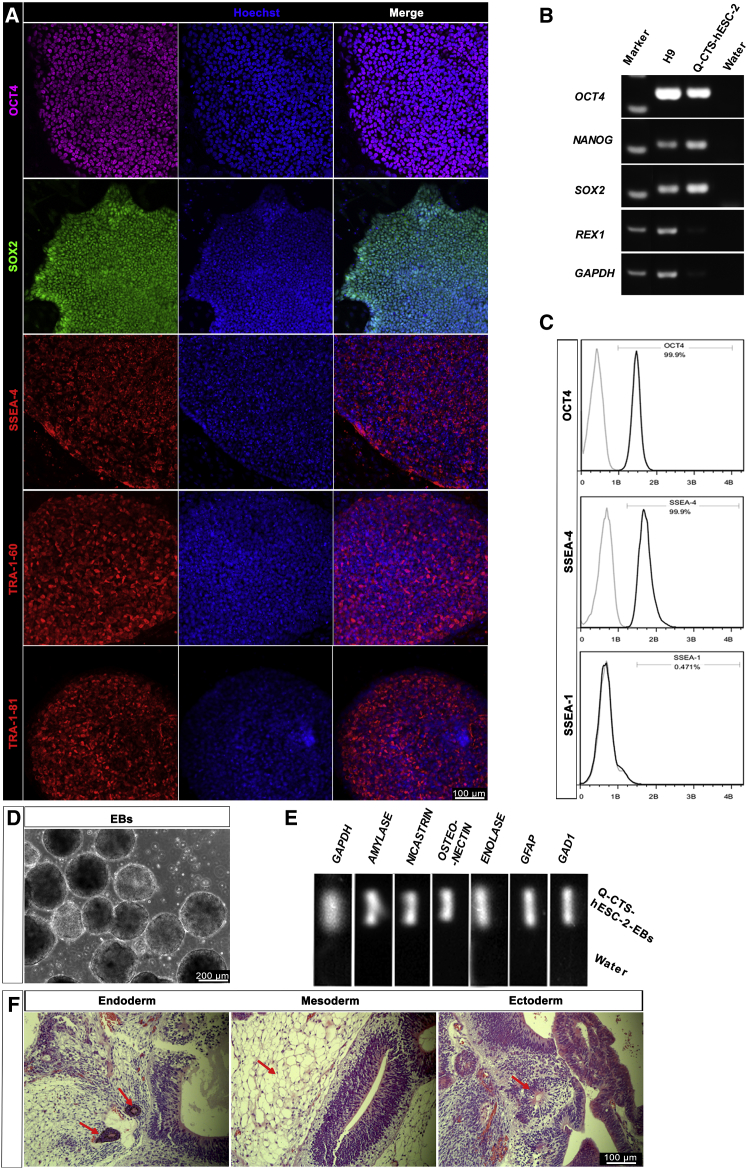
Figure 3.
Pluripotent Characterization of Q-CTS-hESC-2 Cells
(A) Immunofluorescence analysis of Q-CTS-hESC-2 cells. Positive nuclear transcription factors OCT4 (purple) and SOX2 (green) and clear expression of the ESC surface antigen SSEA4 (red), TRA-1-60 (red), and TRA-1-81 (red) were observed. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(B) RT-PCR analysis confirmed the expression of the ESC-specific genes (OCT4, NANOG, SOX2, and REX1). H9 cells were used as a positive control and water as the negative control. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping gene.
(C) Quantitative flow-cytometry analysis indicating robust expression of intracellular OCT4 and extracellular SSEA4 with almost no SSEA1 in feeder-free Q-CTS-hESC-2 cells.
(D) Q-CTS-hESC-2 cells can form EBs after suspension culture.
(E) RT-PCR of EBs showing transcripts for ectoderm (GAD1 and GFAP), mesoderm (ENOLASE and OSTEONECTIN), and endoderm (AMYLASE and NICASTRIN, also named NCSTN) markers.
(F) Teratoma formation. All three germ layer tissues were present on the teratoma dissection slices identified by staining with H&E. The red arrows indicate endoderm with glands (left), mesoderm with fat tissues (middle), and ectoderm with nervous tissues (right). Scale bars, 100 μm.