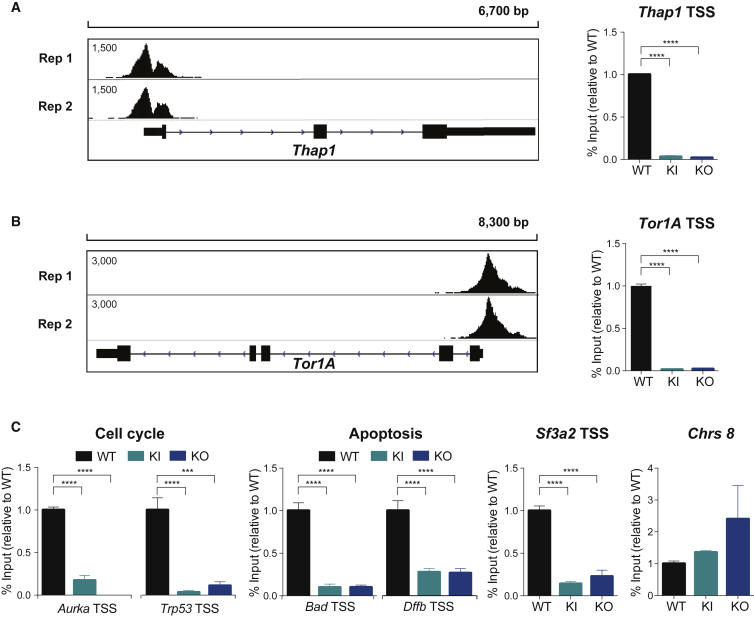
Figure 5.
ChIP and qRT-PCR Validation of THAP1 Target Genes
(A) ChIP-Seq binding profiles for THAP1 replicates (Rep) 1 and 2 at the Thap1 locus (left panel). ChIP qRT-PCR analysis of THAP1 at Thap1 TSS in WT, Thap1C54Y/C54Y (KI), and Thap1ΔExon2 (KO) ESCs (right panel). Data are normalized to percent input and relative to WT. An ANOVA was performed, which revealed a significant difference among the genotypes when examining THAP1 binding (F(2,8) = 1544, p < 0.0001). Holm-Sidak's multiple comparisons test was performed post hoc, revealing significant differences between the genotypes. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(B) ChIP-Seq binding profiles for THAP1 replicates (Rep) 1 and 2 at the Tor1A locus (left panel). ChIP qRT-PCR analysis of THAP1 at Tor1A TSS in WT, Thap1C54Y/C54Y (KI), and Thap1ΔExon2 (KO) ESCs (right panel). Data are normalized to percent input and relative to WT. An ANOVA was performed, which revealed a significant difference among the genotypes when examining THAP1 binding (F(2,0) = 1854, p < 0.0001). The Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test was performed post hoc, revealing significant differences between the genotypes. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(C) ChIP-qPCR analysis of THAP1 at cell-cycle genes (Aurka and Trp53), apoptosis (Bad and Dffb), and Sf3a2 TSS in WT, Thap1C54Y/C54Y (KI), and Thap1ΔExon2 (KO) ESCs. Chromosome 8 was used as a negative control. Data are normalized to percent input and relative to WT. Significant differences were observed among the genotypes when examining the binding of THAP1 at the cell-cycle genes Aurka (F(2,7) = 118.2, p < 0.0001) and Trp53 (F(2,9) = 37.43, p < 0.0001). Significant differences were observed among the genotypes when examining the THAP1 binding at apoptosis related genes Bad (F(2,9) = 74.64, p < 0.0001) and Dffb (F(2,9) = 39.21, p < 0.0001). Significant differences were observed among the genotypes when examining the THAP1 binding at the RNA splicing related gene, Sf3a2 (F(2,9) = 39.21, p < 0.0001). No differences were observed among the genotypes with ANOVA when examining the THAP1 binding at Chrs8. The Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test was performed post hoc, revealing significant differences between the genotypes. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. ∗∗∗p < 0.005, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001.