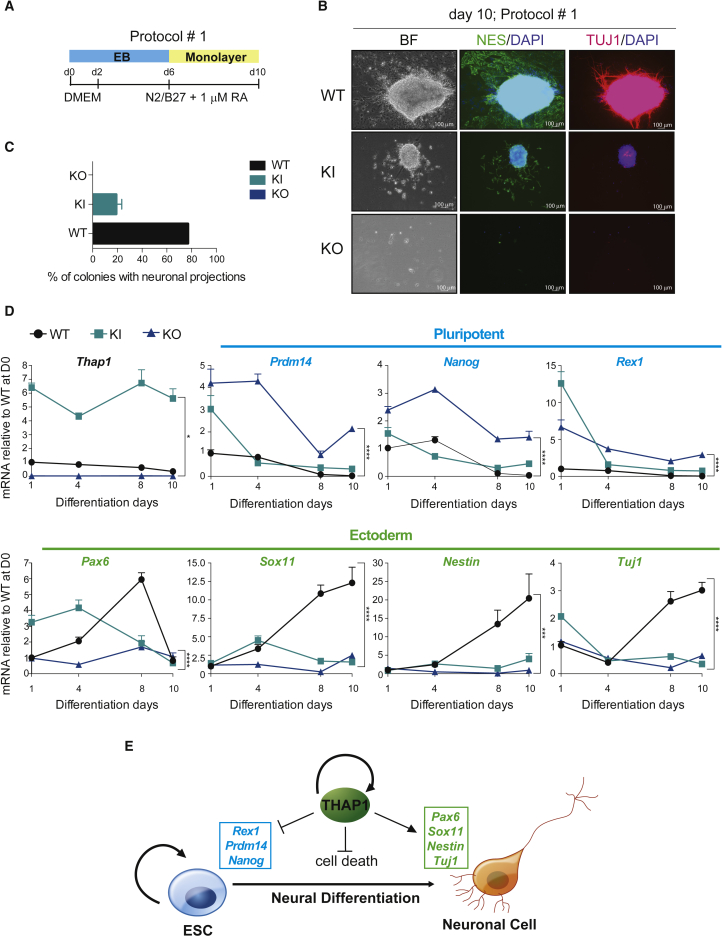
Figure 7.
Characterization of Neural Differentiation
(A) Schematic representation of cell-culture strategy of neural differentiation using protocol #1.
(B) Immunofluorescence analysis of Nestin (green; middle panel) and TuJ1 (red; right panel) of WT, Thap1C54Y/C54Y (KI), and Thap1ΔExon2 (KO) differentiated cells at day 10 of differentiation. Bright field (left panel) and DAPI stain (blue) are shown. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(C) Bar graph depicting percentage of colonies with neuronal projection.
(D) qRT-PCR analysis of Thap1, pluripotent, and ectoderm marker genes during neural differentiation (protocol #1) of Thap1C54Y/C54Y (KI) and Thap1ΔExon2 (KO) ESCs at the indicated time points. Data are presented relative to WT at day 0. The two-way ANOVA results for Thap1, pluripotent, and ectoderm marker genes during RA-induced differentiation can be found in Table S3. The Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test was performed post hoc for each gene of interest by day, revealing significant differences between the genotypes. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.005, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(E) Schema illustrating that THAP1 is required to silence the expression of the pluripotency factors and to activate the expression of the neural factors, as well as mediate ESC survival.