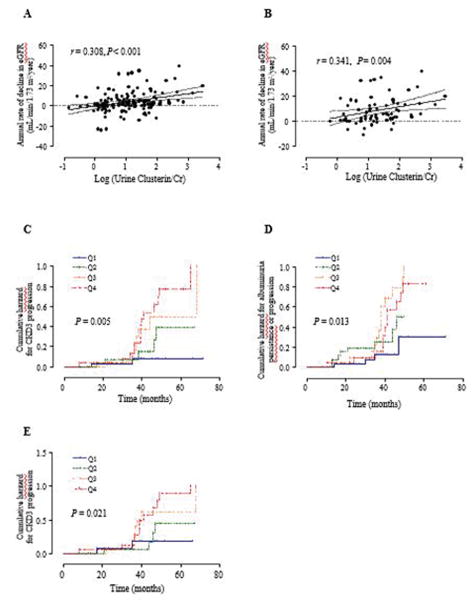
Figure 1.
Single regression analysis of the annual rate of decline in eGFR using urine clusterin in patients with all type 2 diabetic patients (A) and those with albuminuria (B). Cumulative incidences of CKD stage 3 or greater (eGFR <60mL/min/1.73 m2) (C) and persistence/progression for albuminuria (D) using the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test in all type 2 diabetic patients according to urine Clusterin/Cr quartile (Q1 to Q4). Cumulative incidences of CKD stage 3 or greater (eGFR <60mL/min/1.73 m2) in those with albuminuria (E) according to urine Clusterin/Cr quartile. Logarithm-transformed value of urine Clusterin/Cr was used for analysis. Cr, creatinine; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate. CKD, chronic kidney disease; Q, quartile.