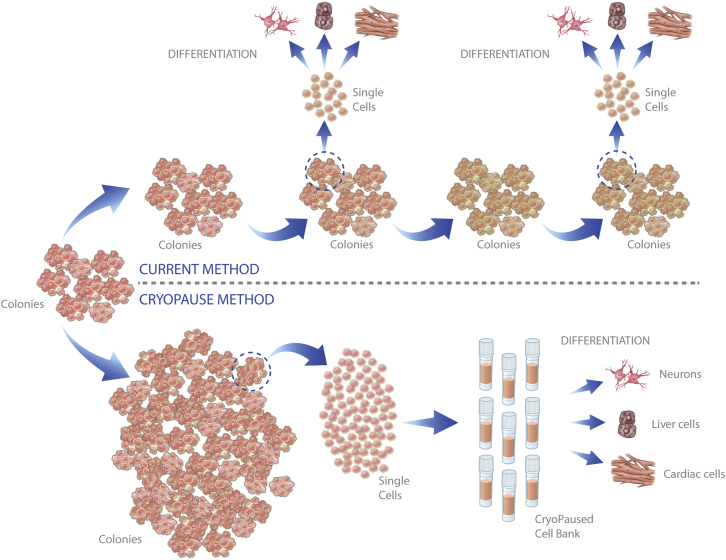
Figure 1.
The CryoPause Method Compared with Conventional PSC Culture
(Top) The conventional (control) workflow recovers colonies from cryopreservation and expands them over long periods of time, periodically using a portion of the culture for specific applications such as directed differentiation into a cell type of interest. Over time, PSCs might acquire genetic changes, contamination, or changes in the amount of spontaneous differentiation, any of which could affect results. (Bottom) CryoPause expands a large pool of PSCs over the least number of passages possible. The large batch is then dissociated into a single-cell suspension before cryopreservation. The freezing process separates the production of PSCs from their use, allowing time to perform proper quality control and characterization of each bank. It also permits the use of identical cells in multiple experiments, and allows shipping anywhere in the world so that other laboratories can initiate independent experiments with the exact same starting population of PSCs.