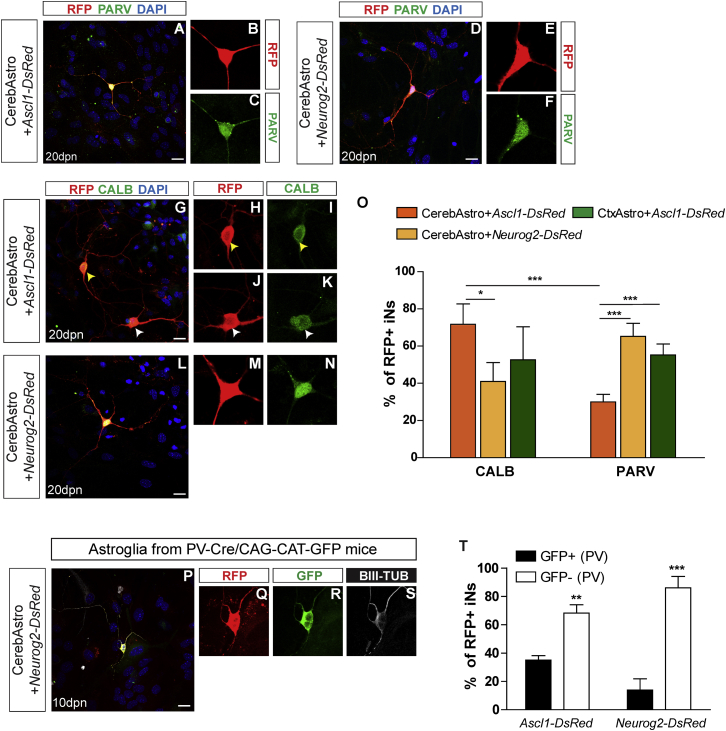
Figure 4.
Expression of Calcium Binding Proteins Indicates that iNs Derived from Cortical and Cerebellar Astroglia Adopt Distinct GABAergic Phenotypes
(A–N) Examples of CerebAstro-derived iNs expressing PARV or CALB 30 dpn with either ASCL1 (A and G) or NEUROG2 (D and L). Single confocal z stacks of the two iNs (white and yellow arrowheads) are shown in higher magnification to confirm the colocalization of RFP with PARV (B, C, E, and F) or CALB (H–K, M, and N).
(O) Quantification of CALB+ and PARV+ cells among RFP+ iNs derived from both CerebAstro nucleofected with either ASCL1 (orange) or NEUROG2 (yellow) and CtxAstro nucleofected with ASCL1 (green). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(P) Example of NEUROG2-iN reprogrammed from CerebAstro isolated from PARV-Cre/CAG-CAT-GFP mice.
(Q–S) Single confocal z stacks are shown in higher magnification to confirm the colocalization of RFP, GFP, and BIII-TUB.
(T) Quantification of ASCL1-iNs and NEUROG2-iNs expressing GFP after lineage reprogramming of PARV-Cre/CAG-CAT-GFP CerebAstro (two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test, mean ± SEM). CALB, CALBINDIN; PARV, PARVALBUMIN; TUB, TUBULIN. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
Data are derived from three independent experiments. Scale bars, 20 μm. See also Figure S6.